On January 6 2021, supporters of former US President Donald J. Trump invaded the Capitol and held lawmakers hostage for hours.
Their goal: to disrupt the confirmation of the November 2020 Presidential elections.
While this behavior can be traced to unverified claims of election fraud spread online, the event represented something more fundamental: dwindling trust in the ability of governments to conduct free and fair elections.
Put simply, citizens don’t think the current centralized system of voting can assure the credible election of candidates.
As a system built on citizen participation, democracy may be destroyed if individuals refuse to vote because they don’t trust the election process.
The blockchain is a distributed, unalterable, and public ledger of transactions. Blockchain technology promotes anonymity, security, and immutability of data transactions.
Can the qualities of blockchain technology be adapted to modern-day voting systems to improve election integrity? Many people certainly think this is possible.
This article will cover the basics of blockchain technology and its applications to voting systems. We’ll also look at the merits of blockchain voting and explore the challenges of voting on the blockchain.
How Does Blockchain Work?
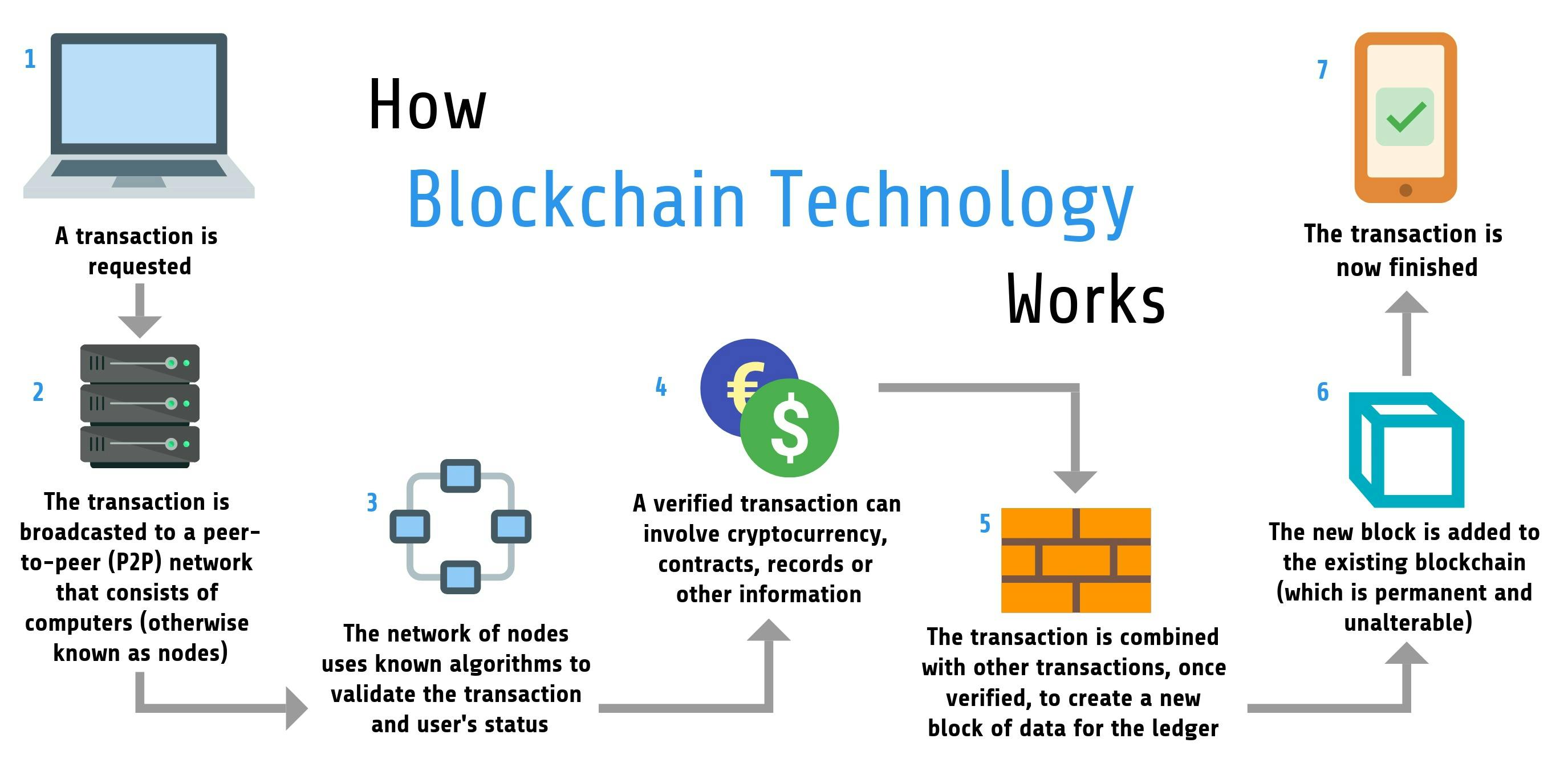
To understand the appeal of blockchain voting systems, it’s important to know how the technology itself works. Here’s a basic ELI5 description of blockchain technology:
The blockchain is a record of transactions stored on a distributed network of computers called nodes. Every node on the blockchain can add transactions or query newly added transactions on the chain.

Before transactions are added to the blockchain, a subset of nodes (called miners) must solve cryptographic puzzles to win the right to validate transactions. Afterward, transactions are bundled into “blocks” and added to the ledger.
Blocks have unique fingerprints called “hashes.” The hash value for each block is linked to its transaction data, so any attempt to alter block data will alter the hash as well.
Also, every block’s hash is generated based on the hash of the previous block. This makes it impossible to change a block’s hash without changing the hash of the previous block. Thus, we can understand how the blockchain protects the integrity of on-chain data.
Transactions on a blockchain are irreversible and data cannot be erased or deleted. In the context of an election, this means votes cannot be deleted as is possible with current electronic voting machines (EVMs).
Moreover, blockchain transactions are anonymous and highly secure. Each user has a wallet that they can use to store tokens, cryptocurrencies, and other forms of digital data.
Using asymmetric cryptography, the blockchain creates a pair of keys for each user.
The first, called a public key, is used to generate a public address for each participant on the network (think of it as a personal ID badge). Meanwhile, the second key (private key) is used to “sign” transactions. This key is kept secure and cannot be shared with others.
Public addresses on the blockchain are like IP addresses: no one can know who owns them. This allows people to transact without fear of exposure. For voters, it provides maximum anonymity and privacy in an election.
The use of private keys to generate digital signatures preserves the integrity of on-chain transactions. Since each holder holds their private keys, we can be sure that no one else conducted the transaction by proxy. This can help reduce problems of voter verification during elections.
How blockchain transactions work
Image source: Quora
What is Blockchain Voting?
Blockchain voting is an application of blockchain technology to improve election processes. A blockchain voting system typically has some or all of the following features:
-
Decentralization: The blockchain is stored on a peer-to-peer system of computers scattered across different locations, not a central server. A blockchain voting system is more…
Read More: web3.hashnode.com









 Bitcoin
Bitcoin  Ethereum
Ethereum  XRP
XRP  Tether
Tether  Solana
Solana  Dogecoin
Dogecoin  USDC
USDC  Cardano
Cardano  Lido Staked Ether
Lido Staked Ether  TRON
TRON  Avalanche
Avalanche  Wrapped stETH
Wrapped stETH  Sui
Sui  Chainlink
Chainlink  Toncoin
Toncoin  Shiba Inu
Shiba Inu  Stellar
Stellar  Wrapped Bitcoin
Wrapped Bitcoin  Hedera
Hedera  Polkadot
Polkadot  WETH
WETH  Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash  Uniswap
Uniswap  Pepe
Pepe  Litecoin
Litecoin  Hyperliquid
Hyperliquid  LEO Token
LEO Token  Wrapped eETH
Wrapped eETH  NEAR Protocol
NEAR Protocol  Internet Computer
Internet Computer  Ethena USDe
Ethena USDe  USDS
USDS  Aptos
Aptos  Aave
Aave  Mantle
Mantle  Render
Render  Bittensor
Bittensor  Cronos
Cronos  POL (ex-MATIC)
POL (ex-MATIC)  Ethereum Classic
Ethereum Classic  Artificial Superintelligence Alliance
Artificial Superintelligence Alliance  Virtuals Protocol
Virtuals Protocol  WhiteBIT Coin
WhiteBIT Coin  MANTRA
MANTRA  Arbitrum
Arbitrum  Monero
Monero  Tokenize Xchange
Tokenize Xchange