[ad_1]

Today’s guide will dive into the intricacies of ETH getLogs and show you how to use this JSON-RPC method in practice. However, there are multiple ways to get Ethereum logs, and while our focus is on getLogs, we’re also going to compare this method to Moralis’ getContractLogs() endpoint. For a quick start, here are two examples of what both of them look like in action:
{ "jsonrpc": "2.0", "id": 0, "method": "eth_getLogs", "params": [ { "fromBlock": "0x429d3b", "toBlock": "0x429d3b", "address": "0xb59f67a8bff5d8cd03f6ac17265c550ed8f33907", "topics": [ "0xddf252ad1be2c89b69c2b068fc378daa952ba7f163c4a11628f55a4df523b3ef", "0x00000000000000000000000000b46c2526e227482e2ebb8f4c69e4674d262e75", "0x00000000000000000000000054a2d42a40f51259dedd1978f6c118a0f0eff078" ] } ] } { "id": 0, "jsonrpc": "2.0", "result": [ { "address": "0xb59f67a8bff5d8cd03f6ac17265c550ed8f33907", "blockHash": "0x8243343df08b9751f5ca0c5f8c9c0460d8a9b6351066fae0acbd4d3e776de8bb", "blockNumber": "0x429d3b", "data": "0x000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000012a05f200", "logIndex": "0x56", "removed": false, "topics": [ "0xddf252ad1be2c89b69c2b068fc378daa952ba7f163c4a11628f55a4df523b3ef", "0x00000000000000000000000000b46c2526e227482e2ebb8f4c69e4674d262e75", "0x00000000000000000000000054a2d42a40f51259dedd1978f6c118a0f0eff078" ], "transactionHash": "0xab059a62e22e230fe0f56d8555340a29b2e9532360368f810595453f6fdd213b", "transactionIndex": "0xac" } ] } - Example of
getContractLogs():
const response = await Moralis.EvmApi.events.getContractLogs({ "chain": "0x1", "topic0": "0xddf252ad1be2c89b69c2b068fc378daa952ba7f163c4a11628f55a4df523b3ef", "address": "0xb47e3cd837dDF8e4c57F05d70Ab865de6e193BBB" }); //… "result": { "transaction_hash": "0x2d30ca6f024dbc1307ac8a1a44ca27de6f797ec22ef20627a1307243b0ab7d09", "address": "0x057Ec652A4F150f7FF94f089A38008f49a0DF88e", "block_timestamp": "2021-04-02T10:07:54.000Z", "block_number": 12526958, "block_hash": "0x0372c302e3c52e8f2e15d155e2c545e6d802e479236564af052759253b20fd86", "data": "0x00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000de05239bccd4d537400000000000000000000000000024dbc80a9f80e3d5fc0a0ee30e2693781a443", "topic0": "0x2caecd17d02f56fa897705dcc740da2d237c373f70686f4e0d9bd3bf0400ea7a", "topic1": "0x000000000000000000000000031002d15b0d0cd7c9129d6f644446368deae391", "topic2": "0x000000000000000000000000d25943be09f968ba740e0782a34e710100defae9", "transaction_index": 12, "log_index": 15 } If you would like to learn more about getLogs and the getContractLogs() endpoint, read on or check out our official eth_getLogs documentation!
Overview
In today’s article, we’ll start by covering the basics and explaining the ins and outs of Ethereum logs. In doing so, we’re going to explore the central components of all Ethereum logs and where they are stored. From there, we’ll dive into ETH getLogs and give you a practical example of how this method works. We’ll then cover some prominent getLogs use cases to give you an idea of how to use Ethereum logs in your development endeavors. Lastly, to top things off, we’ll dive into Moralis and the getContractLogs() endpoint, as this is an even more convenient alternative for fetching Ethereum logs!
Furthermore, getting Ethereum logs is only one aspect of blockchain development. So, if you’re serious about building Web3 projects, we urge you to check out additional development tools, including Moralis’ industry-leading Web3 API suite, to help you build faster and more effectively. For example, if you have ambitions to build NFT-based platforms, you can take advantage of the Moralis NFT API. With this programming interface, you can effortlessly get all NFT tokens owned by a user address, get ERC-721 on-chain metadata, etc., with only single lines of code!
When working with Moralis, it has never been easier to build Web3 projects. So, before you continue, make sure to sign up with Moralis. You can create an account for free, and you’ll be able to immediately start leveraging the full power of blockchain technology!
Nevertheless, without further ado, let’s jump straight into this article and explore the intricacies of Ethereum logs!
Understanding getLogs – What are Ethereum Logs?
Ethereum smart contracts store information in two distinct ways: account storage and logs. The account storage contains all the data defining the smart contract state, while logs store information that isn’t required by the contract but can be accessed by other off-chain systems like web applications.
But what exactly are Ethereum logs? And how do they work?

Most Ethereum smart contracts emit events whenever they execute. When this occurs, the contracts additionally generate logs appertaining to the events in question. These logs provide valuable insight into each event, making them crucial for Web3 development.
Here are the major components of an Ethereum event log:
- Event Signature: A unique identifier for the log’s event. It’s generated by hashing the event’s name and its parameter types using the Keccak-256 hash function.
- Contract Address: The address of the smart contract that emitted the event.
- Topics: An array of indexed parameters providing details regarding the event. Ethereum logs can have a maximum of four topics. The first one is required, and it always contains the event signature. The remaining three are optional and are typically used for indexing and providing faster lookup times.
- Data: An unlimited field for encoded hex data relevant to the event. If the information doesn’t get indexed into the topics array, it will, by default, automatically end up in the data field. The data field can contain any data type, including strings, integers, and arrays.
- Block Number: The number of blocks in the blockchain where the event was triggered.
- Transaction Hash: The hash of the transaction that triggered the event.
If you want to dive deeper into this topic, check out our article on Ethereum logs and events!
Where are Ethereum Logs Stored?
Whenever Ethereum smart contracts emit events, the logs are written and stored in so-called transaction receipts. Each transaction has only one receipt, and in addition to an Ethereum event log, it also includes other data like status, gas used for the transaction, log blooms, etc.
Now, with a brief overview of Ethereum logs and where they are stored, let’s take a closer look at how you can acquire them!
What is ETH getLogs?
ETH getLogs is the gateway to Ethereum events, and it’s a JSON-RPC method returning an array of all logs matching a specified filter. The use of eth_getLogs plays an integral role in the blockchain industry, empowering developers by providing a valuable tool for monitoring and analyzing events that occur on the Ethereum blockchain.

With this method, you get a seamless way to access information such as the topics and data of Ethereum logs. As you can imagine, this is vital information when building decentralized applications (dapps) interacting with smart contracts.
To get a more in-depth understanding of the eth_getLogs method, let’s look at a practical example in the next section!
Example: How to Use ETH getLogs During Ethereum Development
In this section, we’ll cover a brief example where we make an eth_getLogs request for a hypothetical smart contract. The smart contract has a straightforward transfer event that looks like this: Transfer(address,address,unit256). Here’s an example of what the request might look like:
{ "jsonrpc": "2.0", "id": 0, "method": "eth_getLogs", "params": [ { "fromBlock": "0x429d3b", "toBlock": "0x429d3b", "address": "0xb59f67a8bff5d8cd03f6ac17265c550ed8f33907", "topics": [ "0xddf252ad1be2c89b69c2b068fc378daa952ba7f163c4a11628f55a4df523b3ef", "0x00000000000000000000000000b46c2526e227482e2ebb8f4c69e4674d262e75", "0x00000000000000000000000054a2d42a40f51259dedd1978f6c118a0f0eff078" ] } ] } In the code above, we make an eth_getLogs request with four parameters: fromBlock, toBlock, address, and topics. The fromBlock and toBlock parameters specify the blocks we want to restrict our query to; meanwhile, address specifies the address of the smart contract we want to get the log for.
The topics array, in this case, contains three elements. The first one is the event signature of the smart contract’s transfer event. The second and third elements specify two addresses, and we’re specifically querying for transfer events between them.
Now, let’s take a closer look at the response of our eth_getLogs request:
{ "id": 0, "jsonrpc": "2.0", "result": [ { "address": "0xb59f67a8bff5d8cd03f6ac17265c550ed8f33907", "blockHash": "0x8243343df08b9751f5ca0c5f8c9c0460d8a9b6351066fae0acbd4d3e776de8bb", "blockNumber": "0x429d3b", "data": "0x000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000012a05f200", "logIndex": "0x56", "removed": false, "topics": [ "0xddf252ad1be2c89b69c2b068fc378daa952ba7f163c4a11628f55a4df523b3ef", "0x00000000000000000000000000b46c2526e227482e2ebb8f4c69e4674d262e75", "0x00000000000000000000000054a2d42a40f51259dedd1978f6c118a0f0eff078" ], "transactionHash": "0xab059a62e22e230fe0f56d8555340a29b2e9532360368f810595453f6fdd213b", "transactionIndex": "0xac" } ] } As you can see, the response provides a lot of information. However, in this case, we’re primarily interested in the topics and data fields. As you’ll quickly notice, the topics array remains the same as in our eth_getLogs request. Consequently, the first topic is the event signature, while the remaining two are the from and to addresses of the transfer.
The other field of interest is data, which contains all the additional information that hasn’t been indexed. In this case, it is the uint256 parameter of the event, and it represents the transaction’s transfer amount.
You can learn more about each contract and what the data in the response means by studying the contract’s ABI. For instance, this is what the transfer event ABI reference looks like for our example contract:
{ "anonymous": false, "inputs": [ { "indexed": true, "name": "from", "type": "address" }, { "indexed": true, "name": "to", "type": "address" }, { "indexed": false, "name": "value", "type": "uint256" } ], "name": "Transfer", "type": "event" }, That’s it! This covers our simple example of how to use getLogs during Ethereum development!
Use Cases for ETH getLogs
Now, with an overview of Ethereum logs and how the ETH getLogs method works, let’s take a closer look at what it’s used for in Web3 development. There are multiple use cases for the Ethereum getLogs method, and we won’t have time to cover them all in this tutorial. Therefore, we’ll narrow it down to the following three examples:
- Asynchronous Triggers: When building Web3 projects, your platforms generally need to monitor relevant Ethereum smart contract events. By using the
getLogsmethod, you can leverage Ethereum logs as a form of asynchronous triggers containing data. This will allow your dapps to interact with smart contracts to display certain messages, perform actions, or any other associated tasks.
- Debugging: The ETH
getLogsmethod can be used for debugging smart contracts. For instance, if a smart contract isn’t working as intended, you can leverage thegetLogsmethod to retrieve the events and logs emitted by the contract to identify why the issue is occurring.
- Analytics: You can also leverage the ETH
getLogsmethod to get and analyze smart contract data. An example here is that you can usegetLogsto analyze the volume of trades on a DEX like Uniswap.
However, the three use cases above are just a few prominent examples, and you can do a lot more with getLogs!
An Ethereum getLogs Alternative
One of the drawbacks of the ETH getLogs method is that it requires complicated and detailed setups with JSON RPC calls, which can become quite complex. As such, in this section, we’ll explore Moralis and one of its popular APIs from its Web3 data API suite, the Block API – a more convenient alternative to getLogs!

With the Moralis Block API, you can seamlessly retrieve and analyze Ethereum event logs with a single line of code. The getContractLogs() endpoint stands out as a hallmark of convenience, giving you, as a developer, a more effective way to access Ethereum logs.
To illustrate the accessibility of this tool, we’ll provide a three-step tutorial on how to get Ethereum logs:
1. Get a Moralis API Key
2. Write a Script
3. Execute the Code
However, you must take care of a few prerequisites before you can continue!
Prerequisites
In this brief tutorial, we’ll show you how to get Ethereum event logs using JavaScript. As such, you need to have the following ready before you can continue:
Step 1: Get a Moralis API Key
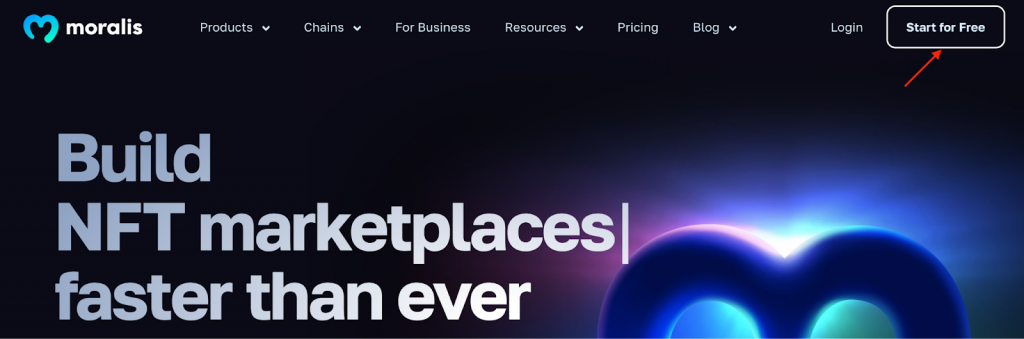
To be able to call the getContractLogs() endpoint, you need a Moralis API key. As such, if you don’t already have one, create your Moralis account immediately by clicking the ”Start for Free” button at the top right:
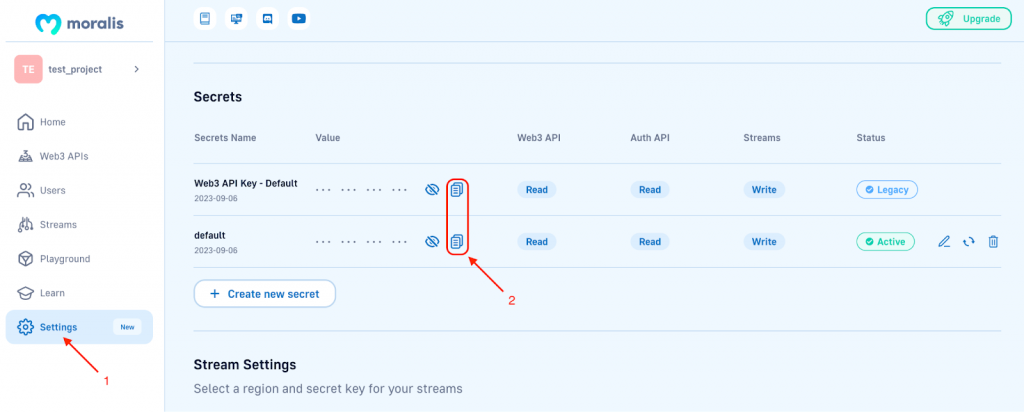
Once you have a Moralis account, you can find your key by navigating to the ”Settings” tab and scrolling down to the ”Secrets” section:
Go ahead and copy your API key, as you’ll need it in the next section.
Step 2: Write a Script
Start by setting up a new project and install the Moralis SDK by running the following terminal command in the root folder:
npm install moralis @moralisweb3/common-evm-utils
Next, create a new ”index.js” file and add the following code:
const Moralis = require("moralis").default; const { EvmChain } = require("@moralisweb3/common-evm-utils"); const runApp = async () => { await Moralis.start({ apiKey: "YOUR_API_KEY", // ...and any other configuration }); const address = "0xb47e3cd837dDF8e4c57F05d70Ab865de6e193BBB"; const chain = EvmChain.ETHEREUM; const topic0 = "0xddf252ad1be2c89b69c2b068fc378daa952ba7f163c4a11628f55a4df523b3ef" const response = await Moralis.EvmApi.events.getContractLogs({ address, chain, topic0, }); console.log(response.toJSON()); }; runApp(); From here, add the API key you copied in the previous step by replacing YOUR_API_KEY:
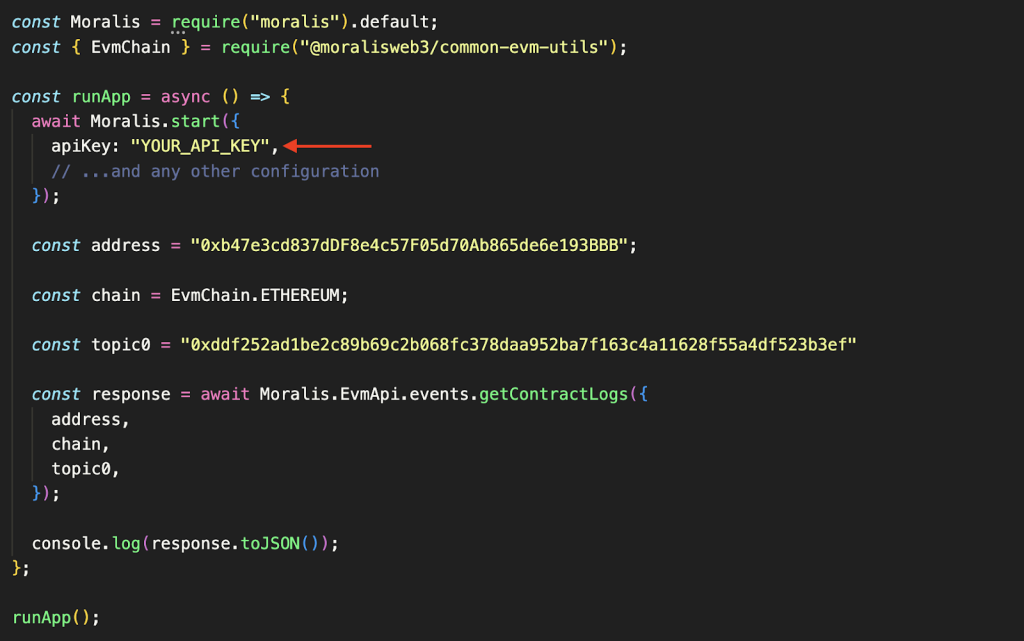
You can then configure the chain, address, and topic0 variables to fit your query. In this case, we simply include the first topic, which, as you might remember, is the event signature:
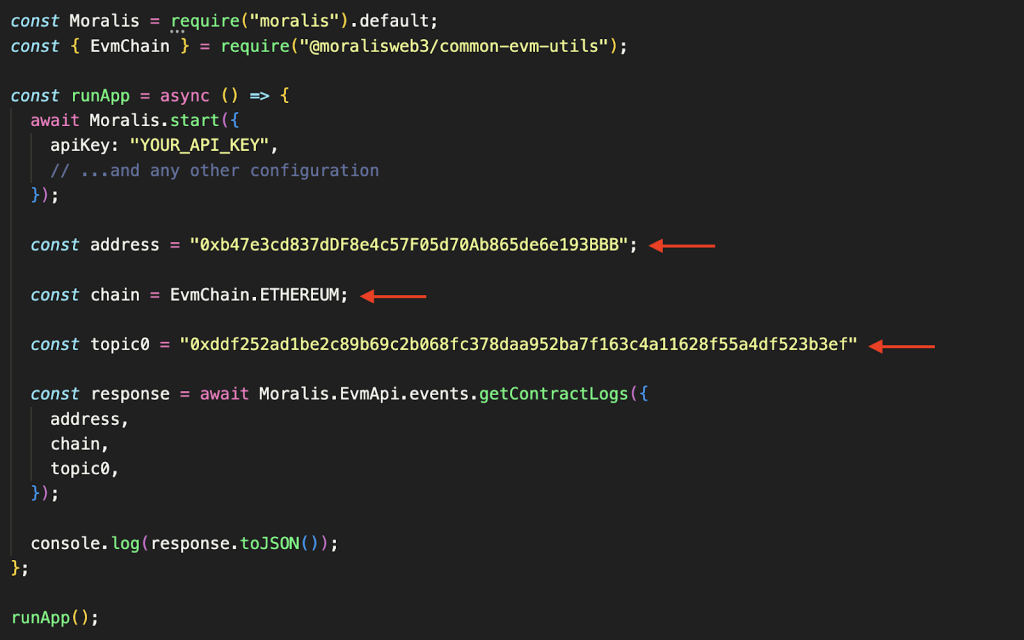
We then take chain, address, and topic0, and pass them as parameters when calling the getContractLogs() endpoint:
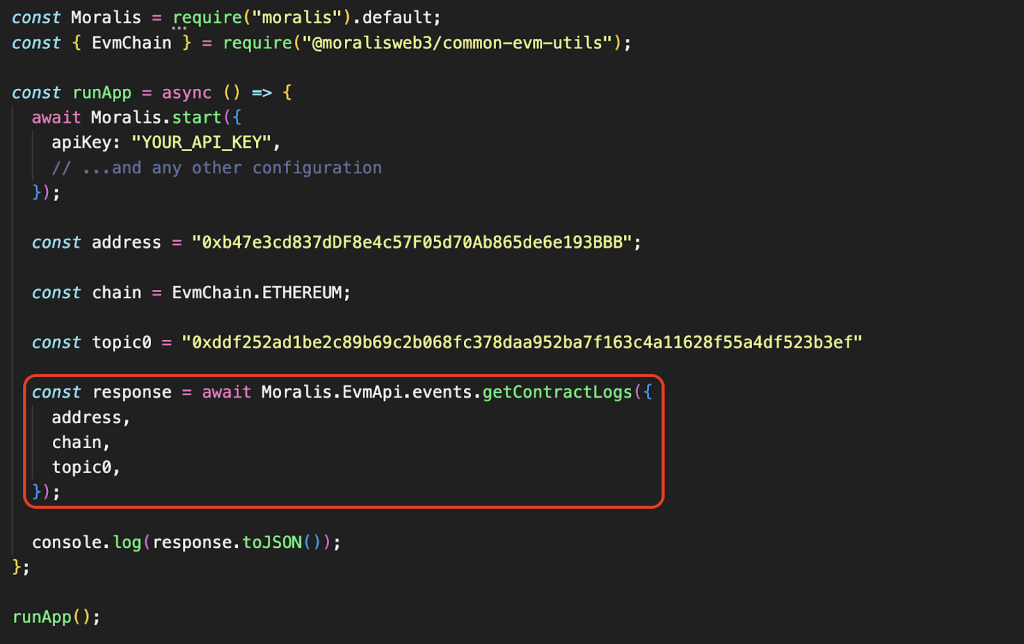
That’s it for the code; you’re now ready to execute the script.
Step 3: Execute the Code
To run the code, simply open a new terminal, cd into the project’s root folder, and run the following command:
node index.js
In return, you’ll get all Ethereum logs based on your request. In our case, the response will look something like this:
//… "result": { "transaction_hash": "0x2d30ca6f024dbc1307ac8a1a44ca27de6f797ec22ef20627a1307243b0ab7d09", "address": "0x057Ec652A4F150f7FF94f089A38008f49a0DF88e", "block_timestamp": "2021-04-02T10:07:54.000Z", "block_number": 12526958, "block_hash": "0x0372c302e3c52e8f2e15d155e2c545e6d802e479236564af052759253b20fd86", "data": "0x00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000de05239bccd4d537400000000000000000000000000024dbc80a9f80e3d5fc0a0ee30e2693781a443", "topic0": "0x2caecd17d02f56fa897705dcc740da2d237c373f70686f4e0d9bd3bf0400ea7a", "topic1": "0x000000000000000000000000031002d15b0d0cd7c9129d6f644446368deae391", "topic2": "0x000000000000000000000000d25943be09f968ba740e0782a34e710100defae9", "transaction_index": 12, "log_index": 15 } //… Congratulations! That’s how easy it is to get Ethereum event logs when working with Moralis and the Block API!
Leveraging Morails and the getContractLogs() endpoint not only simplifies the process of getting Ethereum logs significantly but also enhances efficiency, enabling you to focus on building the best dapps possible!
Summary: What are ETH getLogs?
In today’s article, we kicked things off by exploring the ins and outs of Ethereum logs. In doing so, we learned that each log has the following core components:
- Event Signature
- Contract Address
- Topics
- Data
- Block Number
- Transaction Hash
From there, we showed you how to get Ethereum logs using the Web3 get event logs method: getLogs. As such, if you have followed along this far, you now know how the method works and will be able to integrate Ethereum event logs data into your future projects in no time!
Also, in addition to showing you how getLogs works, we provided you with an alternative in the form of Moralis’ getContractLogs() endpoint, which is an even more convenient way to get Ethereum logs. In fact, we could fetch the data we needed in three straightforward steps:
1. Get a Moralis API Key
2. Write a Script
3. Execute the Code
If you found this article interesting, consider checking out more guides and tutorials here on the Moralis Web3 blog. For instance, learn how to check wallet activity, read about account abstraction, or explore the #1 crypto Market Data API!
Also, before you go, remember to sign up with Moralis. You can create an account completely free and start leveraging the full power of Web3 technology immediately. So, you have nothing to lose!
[ad_2]
Read More: moralis.io








 PinkSale
PinkSale  tokenbot
tokenbot  Bridged USD Coin (Scroll)
Bridged USD Coin (Scroll)  WaterNeuron
WaterNeuron  Covalent X Token
Covalent X Token  OMG Network
OMG Network  Shardus
Shardus  Wen
Wen  Hooked Protocol
Hooked Protocol  Zora
Zora  Magpie
Magpie  cDAI
cDAI  GENIUS AI
GENIUS AI  BBAChain
BBAChain  Sceptre Staked FLR
Sceptre Staked FLR  Infrared BGT
Infrared BGT  Radio Caca
Radio Caca  Advertise Coin
Advertise Coin  Neon
Neon  EarthMeta
EarthMeta  GME (Ethereum)
GME (Ethereum)  GXChain
GXChain  Morphware
Morphware  Gyroscope GYD
Gyroscope GYD  AhaToken
AhaToken  Aegis YUSD
Aegis YUSD  Alien Worlds
Alien Worlds  Heima
Heima  Milady Cult Coin
Milady Cult Coin  Spring Staked SUI
Spring Staked SUI  Step Finance
Step Finance  Avalon
Avalon  Dora Factory
Dora Factory  Laine Staked SOL
Laine Staked SOL  O Intelligence Coin
O Intelligence Coin  Optio
Optio  Noon USN
Noon USN  LUKSO
LUKSO  Coinmetro
Coinmetro  Jambo
Jambo  Guardians Of The Spark
Guardians Of The Spark  Minswap
Minswap  stake.link
stake.link  Camino Network
Camino Network  Port3 Network
Port3 Network