AI has become a part of our lives without us even realizing it. It’s present in the technology that powers our smartphones, the autonomous-driving features in cars, and the tools that retailers use to surprise and delight consumers. Its progress has been gradual and often unnoticed. While there have been notable milestones, like when AlphaGo defeated a world champion Go player in 2016, these achievements quickly faded from public consciousness.

A new wave of generative AI applications is capturing the imagination of people around the world. Unlike AlphaGo, these applications have broad utility and can be used by almost anyone to communicate and create. They possess an uncanny ability to hold conversations with users, making them more accessible and appealing.
These latest generative AI applications can perform various routine tasks such as data reorganization and classification. But it’s their talent for writing text, composing music, and creating digital art that has gained attention and enticed consumers to experiment on their own. As a result, a wider range of people are now grappling with the impact of generative AI on business and society, but often without the necessary context to fully comprehend it.
The speed at which generative AI technology is advancing adds another layer of complexity. ChatGPT was released in November 2022, and just four months later, OpenAI introduced GPT-4, a large language model with significant improvements. Anthropic’s generative AI, Claude, also made significant progress in a short time, being able to process 100,000 tokens of text in a minute by May 2023. Google announced new features powered by generative AI, including Search Generative Experience and PaLM 2, a new language model that will enhance its Bard chatbot and other products.
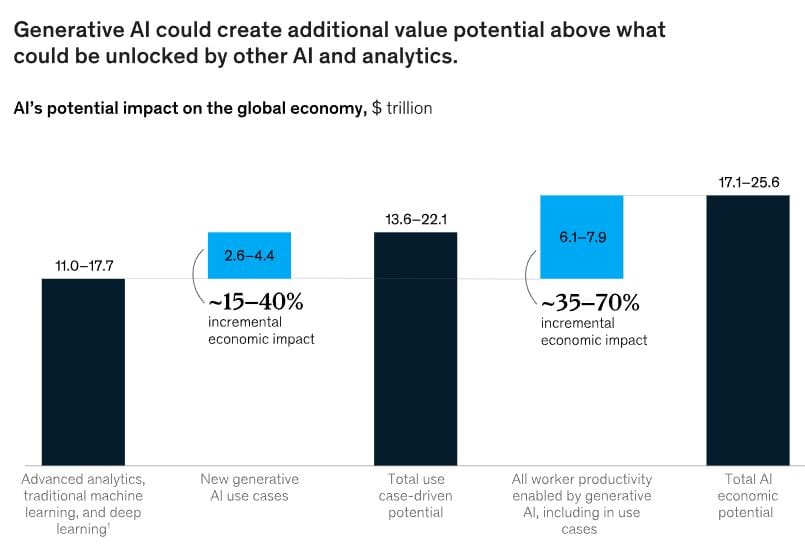
According to a recent report by McKinsey, generative AI is projected to contribute a staggering $4.4 trillion annually to the global economy. This mind-boggling figure highlights the transformative power of AI and its potential to reshape various industries.
The report also sheds light on the shifting timeline for the full automation of work. Previously, experts predicted that AI would automate half of all work between 2035 and 2075. However, the latest findings indicate that this milestone could be achieved as early as 2060. This acceleration in the adoption and implementation of AI technologies demonstrates the rapid pace of development and the far-reaching effects they are having on our society.
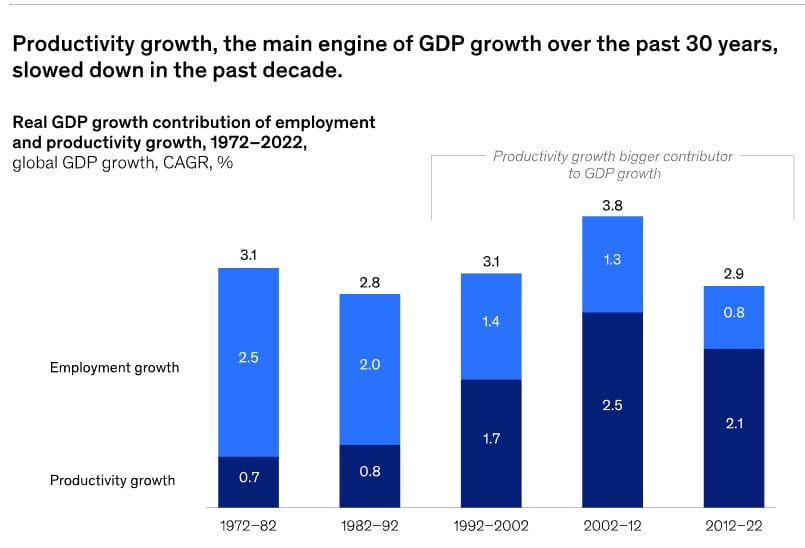
One of the key economic advantages of generative AI lies in its ability to automate work tasks across different sectors. From client interaction and sales to software development and research, AI systems can streamline processes, improve efficiency, and enhance productivity. By taking over routine and repetitive tasks, generative AI allows human professionals to focus on more complex and strategic aspects of their work.
It is critical to address one of the primary concerns about generative AI: the dependability of the content it generates. The report emphasizes the importance of stringent regulation and oversight to ensure that AI-generated content is ethical and trustworthy. As policymakers and organizations recognize the importance of maintaining accountability and accuracy in AI systems, this issue has gained traction and is now receiving the attention it deserves.
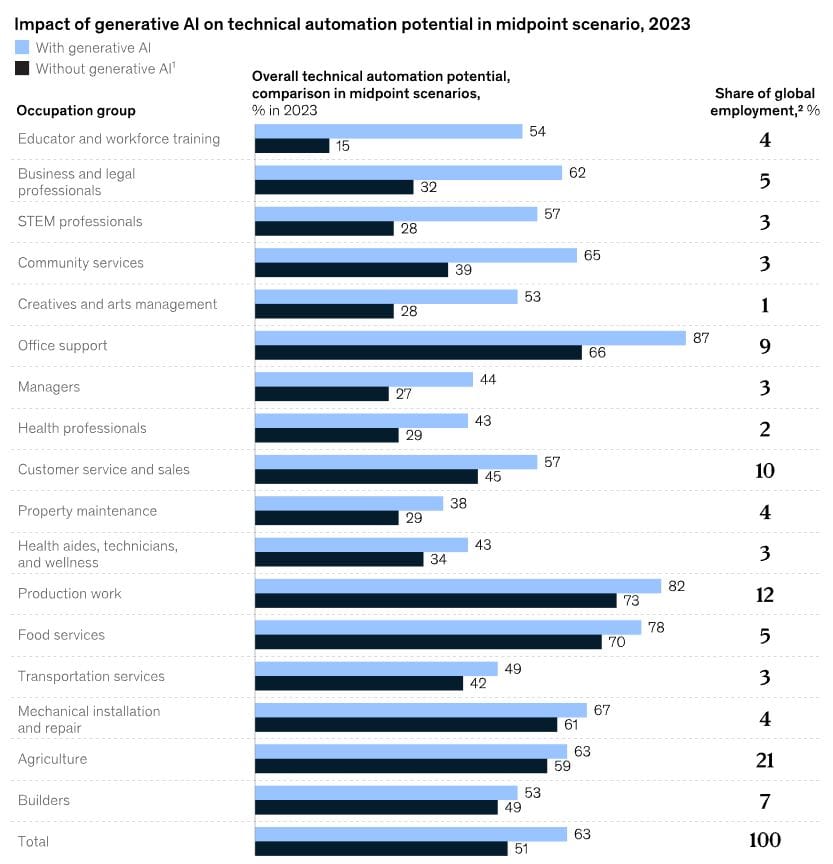
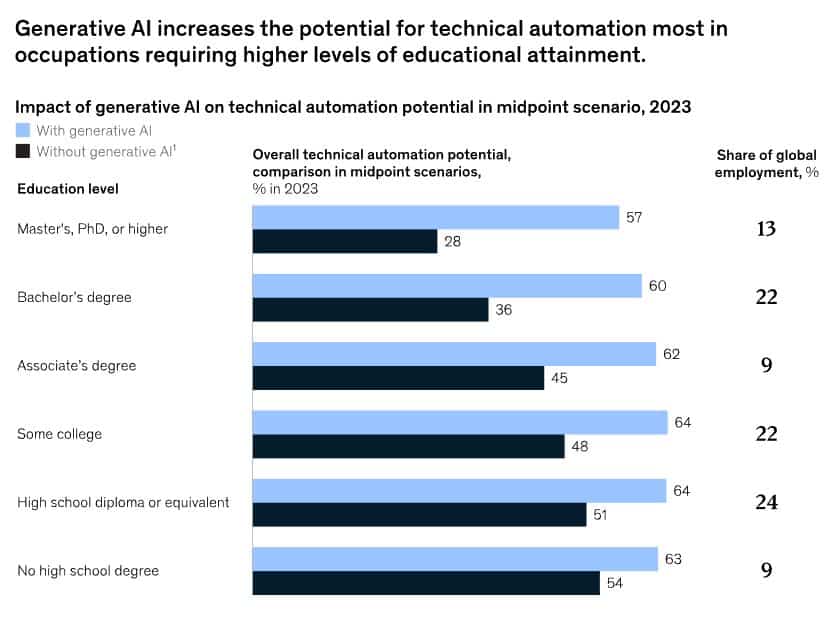
An intriguing observation from the report is the evolving vulnerability of the educated workforce. Traditionally, it was manual occupations that were considered most at risk of automation. With the advent of new technologies like AI, even highly skilled professionals are facing potential disruptions in their industries. This realization underscores the far-reaching impact of AI, as it permeates every sector and transforms the nature of work.
Read more about AI:
Read More: mpost.io









 Bitcoin
Bitcoin  Ethereum
Ethereum  Tether
Tether  XRP
XRP  Solana
Solana  USDC
USDC  Dogecoin
Dogecoin  Cardano
Cardano  TRON
TRON  Lido Staked Ether
Lido Staked Ether  Wrapped Bitcoin
Wrapped Bitcoin  LEO Token
LEO Token  Toncoin
Toncoin  Chainlink
Chainlink  USDS
USDS  Stellar
Stellar  Wrapped stETH
Wrapped stETH  Avalanche
Avalanche  Sui
Sui  Shiba Inu
Shiba Inu  Hedera
Hedera  Litecoin
Litecoin  Polkadot
Polkadot  MANTRA
MANTRA  Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash  Bitget Token
Bitget Token  Ethena USDe
Ethena USDe  Binance Bridged USDT (BNB Smart Chain)
Binance Bridged USDT (BNB Smart Chain)  WETH
WETH  Wrapped eETH
Wrapped eETH  Monero
Monero  WhiteBIT Coin
WhiteBIT Coin  Hyperliquid
Hyperliquid  Pi Network
Pi Network  Uniswap
Uniswap  Dai
Dai  sUSDS
sUSDS  Pepe
Pepe  NEAR Protocol
NEAR Protocol  Aptos
Aptos  OKB
OKB  Coinbase Wrapped BTC
Coinbase Wrapped BTC  Gate
Gate  Tokenize Xchange
Tokenize Xchange  Cronos
Cronos  Ondo
Ondo  Mantle
Mantle  Internet Computer
Internet Computer  Ethereum Classic
Ethereum Classic