[ad_1]
Google has unveiled a language model called AudioPaLM, which combines text-based and speech-based language models to process and generate speech and text seamlessly. By merging the capabilities of PaLM-2 and AudioLM, AudioPaLM offers a unified multimodal architecture that opens up a wide range of applications, including speech recognition and speech-to-speech translation.

One notable feature of AudioPaLM is its ability to preserve paralinguistic information like speaker identity and intonation, thanks to the influence of AudioLM. At the same time, it harnesses the linguistic knowledge found in text-based language models like PaLM-2. By initializing AudioPaLM with the weights of a text-only large language model, the model excels in speech processing, taking advantage of the extensive text training data used in pretraining.
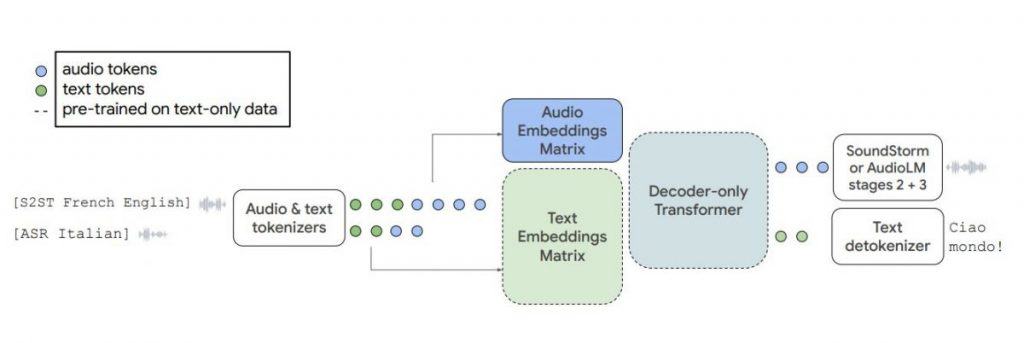
The remarkable capabilities of AudioPaLM have been demonstrated through various experiments. It has outperformed existing systems in speech translation tasks and showcases the ability to perform zero-shot speech-to-text translation for languages not encountered during training.
Additionally, AudioPaLM exhibits features of audio language models by transferring voices across languages based on short spoken prompts.
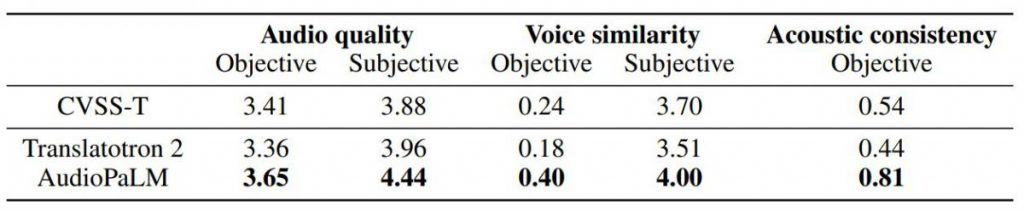
Google has made examples of AudioPaLM’s capabilities available for exploration. The model’s ability to translate languages with distinct accents, such as Italian and German, has intrigued researchers and users alike. Furthermore, its proficiency in performing voice transfers for speech-to-speech translation sets it apart from existing baselines, as confirmed by both automatic metrics and human evaluators.
The model is very good at translating a language from audio to audio in another language, preserving the voice and emotions of a person. Interestingly, When translating some languages like Italian and German, the model has a noticeable accent, and when translating others, for instance, French, it speaks with a perfect American accent.
Read more about AI:
[ad_2]
Read More: mpost.io








 Bitcoin
Bitcoin  Ethereum
Ethereum  Tether
Tether  XRP
XRP  Solana
Solana  USDC
USDC  TRON
TRON  Dogecoin
Dogecoin  Lido Staked Ether
Lido Staked Ether  Cardano
Cardano  Hyperliquid
Hyperliquid  Wrapped Bitcoin
Wrapped Bitcoin  Wrapped stETH
Wrapped stETH  Sui
Sui  Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash  Chainlink
Chainlink  LEO Token
LEO Token  Avalanche
Avalanche  Stellar
Stellar  Toncoin
Toncoin  USDS
USDS  WhiteBIT Coin
WhiteBIT Coin  Shiba Inu
Shiba Inu  Wrapped eETH
Wrapped eETH  WETH
WETH  Litecoin
Litecoin  Hedera
Hedera  Binance Bridged USDT (BNB Smart Chain)
Binance Bridged USDT (BNB Smart Chain)  Monero
Monero  Ethena USDe
Ethena USDe  Polkadot
Polkadot  Bitget Token
Bitget Token  Coinbase Wrapped BTC
Coinbase Wrapped BTC  Uniswap
Uniswap  Pepe
Pepe  Pi Network
Pi Network  Aave
Aave  Dai
Dai  Ethena Staked USDe
Ethena Staked USDe  Bittensor
Bittensor  OKB
OKB  BlackRock USD Institutional Digital Liquidity Fund
BlackRock USD Institutional Digital Liquidity Fund  Aptos
Aptos  Internet Computer
Internet Computer  Cronos
Cronos  NEAR Protocol
NEAR Protocol  Jito Staked SOL
Jito Staked SOL  sUSDS
sUSDS  Ethereum Classic
Ethereum Classic