[ad_1]
Get the best data-driven crypto insights and analysis every week:
We are on the cusp of a significant evolution in the Ethereum blockchain ecosystem with the much-anticipated Dencun upgrade. This update marks a substantial advancement, bolstering Ethereum’s capabilities by addressing some of the ecosystem’s most pressing challenges, such as unlocking Layer-2 scalability and augmenting security for node operators and validators.
In this week’s issue of State of the Network, we delve into the details of the Dencun upgrade. We will explore the nature of the upgrade, the proposed modifications to the Ethereum execution and consensus chains, and the metrics that will help us monitor the progress of this imminent upgrade.
Dencun stands as the moniker for the latest Ethereum upgrade, drawing its name from a unique blend of a celestial body and a geographical location—a convention Ethereum has embraced for its updates. It combines Deneb, a first-magnitude star in the Cygnus constellation, representing the Consensus Layer upgrade, and Cancun the location of Devcon 3, symbolizing the Execution Layer upgrade.
Before rolling out on the main Ethereum network, the Dencun upgrade must be meticulously tested on various Ethereum testnets. This critical phase ensures that all new features work correctly and any potential issues are addressed beforehand. As of now, Dencun has been successfully activated on the Goerli and Sepolia testnets and is scheduled for activation on the remaining testnet, Holešky. These testnet deployments are crucial for thorough testing of all the various clients, especially for developers looking to examine L2 effects related to blob expiry.
The anticipation surrounding the Dencun upgrade is palpable, yet the exact date for its mainnet release is still undisclosed. It’s projected that the upgrade will transition to the mainnet around March or April, subsequent to the 1-2 months of extensive testing in the testnet phase. This meticulous approach highlights Ethereum’s dedication to ensuring stability and reliability, aiming for a seamless and efficient mainnet integration of Dencun.
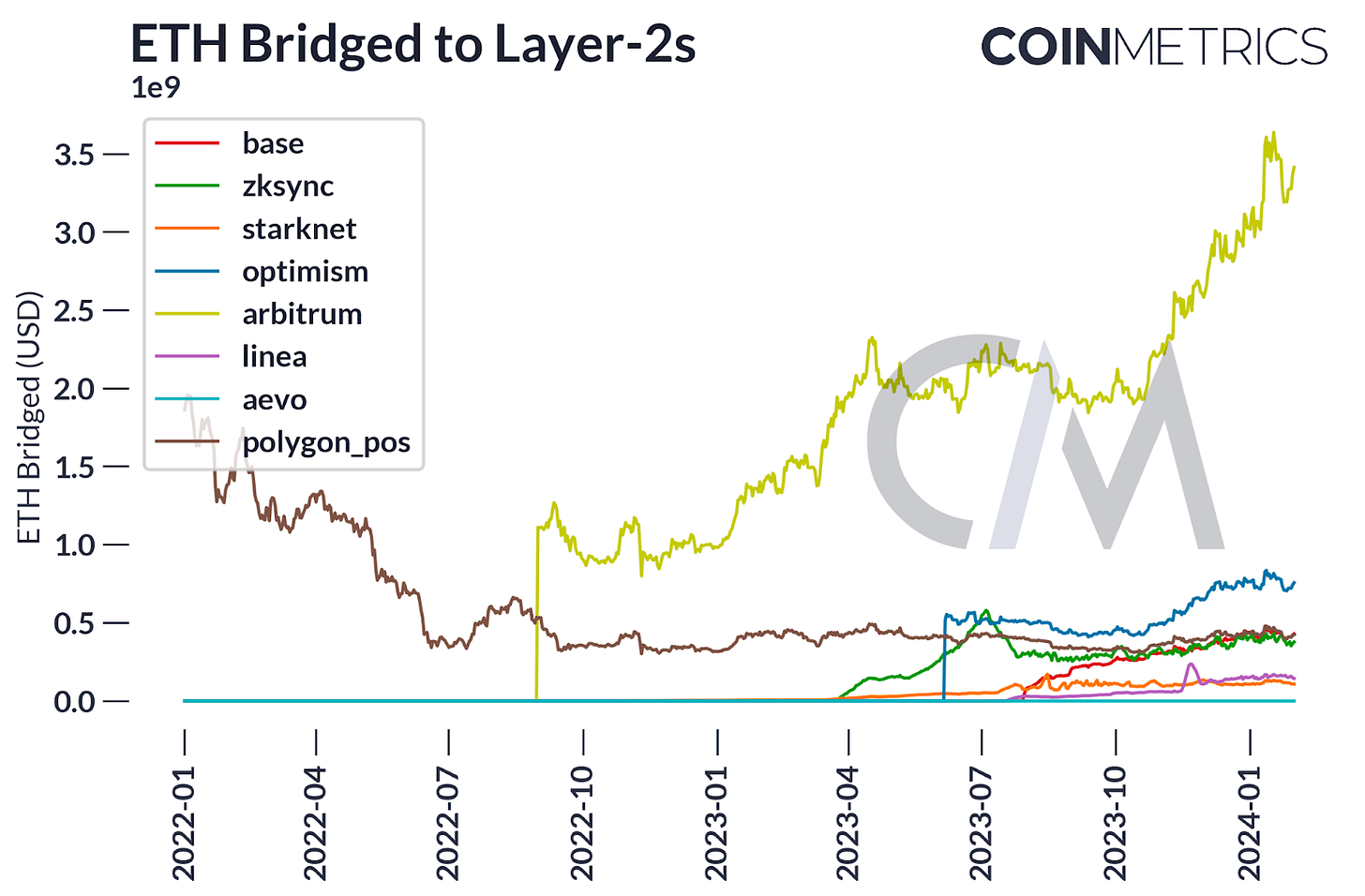
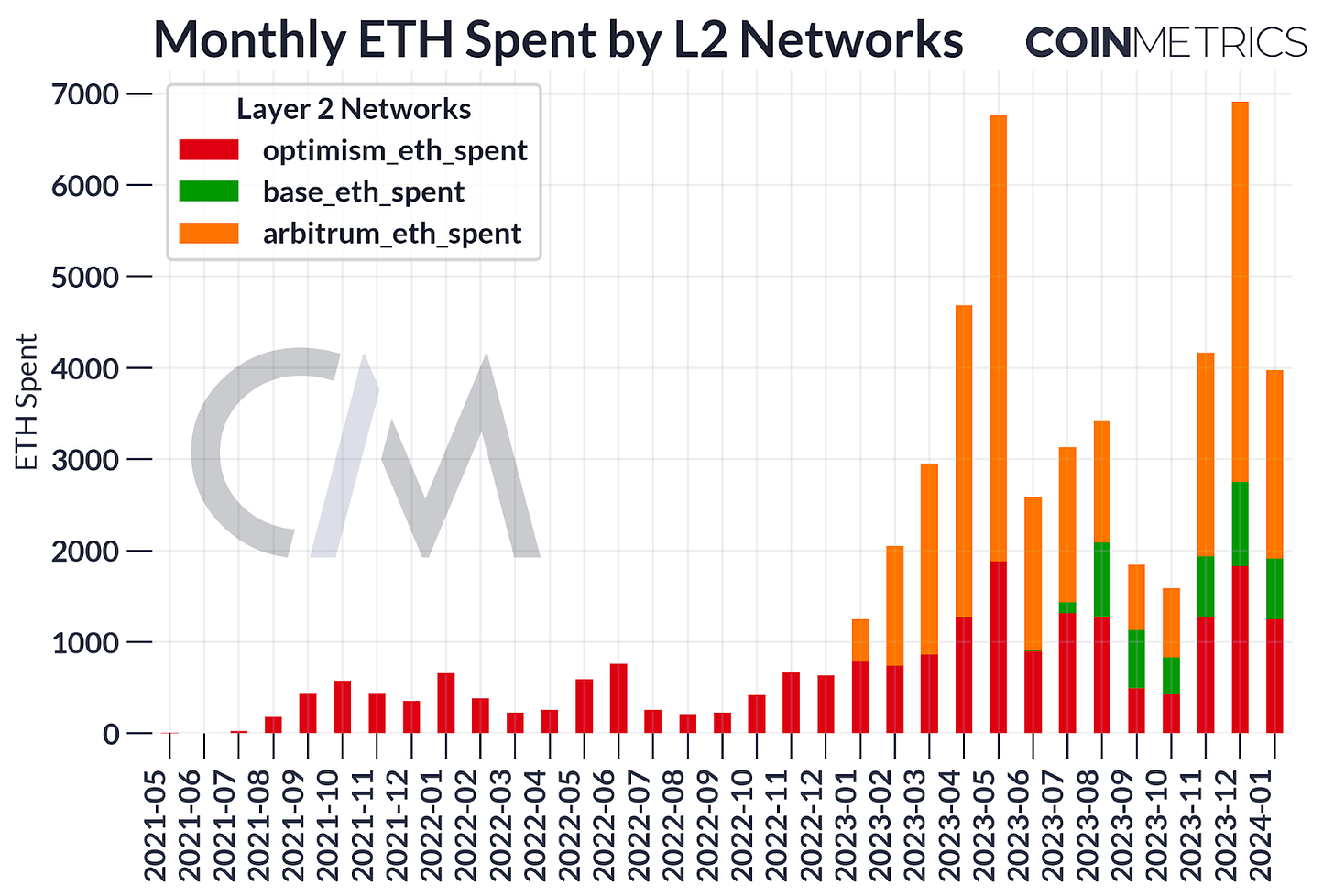
One of the pivotal elements of Dencun is EIP-4844, which introduces “blob-carrying transactions.” These transactions are engineered to enhance data availability scaling within Ethereum. They provide a mechanism for on-chain applications to alleviate L1 fee pressures by shifting demand toward L2s, which are supported by a more economical transaction format for large data blobs. These blobs, while not directly accessible by the EVM, are anchored by commitments that are. The format is devised to be compatible with the anticipated full sharding model, offering interim relief to users who currently bear the brunt of L1 fees.
The proposed EIP lays out specific parameters, cryptographic techniques, and a revamped gas accounting methodology tailored for blob transactions. It further delineates both execution and consensus layer validations, networking implications, and the underpinnings for the inclusion of blob transactions. This EIP is a cornerstone in Ethereum’s scaling strategy and its progression toward sharding, offering a provisional solution that limits the number of these transactions to a cap, aligning with a ~0.375 MB per block target and a ~0.75 MB ceiling.
The Deneb upgrade could potentially reduce Ethereum’s fee revenue in the short-term, as EIP-4844 is set to decrease the fees paid by rollups for block space by over tenfold. The success of this upgrade can be gauged through several indicators, including:
-
Adoption of blob transaction types by L2s
-
Reduction in L2 sequencer fee payments
-
Reduction in transaction fees within L2s
-
Increase in blob fees such that “spam” data is no longer economically feasible
-
Long-term adoption of Ethereum as Data Availability (DA) over competing alternatives, such as Celestia
The expansion of services like Lido and Rocketpool—as well as staking-as-a-service offerings from major players like Coinbase, Binance, and Kraken—has been identified as one of the most significant areas of active research within the Ethereum community to improve the security of the network. Some of these solutions, such as increasing the churn limit will simply decrease the rate at which new validators can join the network.
EIP-4788: Beacon Block Root in the EVM
EIP-4788 proposes embedding the hash tree root of each beacon chain block into the corresponding execution payload header in Ethereum. This involves storing these roots in a smart contract, allowing trust-minimized access to the consensus layer within the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). This information allows purveyors of Liquid Staking Derivatives (LSDs) to reduce the surface area in their operations to issue tokens and rewards (in the case of rebasing tokens that update prices with respect to ETH with prices from a trusted on-chain oracle) in an automated and trustless manner by accessing Consensus Layer data directly.
EIP-7514: Add Max Epoch Churn Limit
As the levels of ETH staked increase, more strain is put on the consensus layer. A larger number of validators leads to an increase in gossip messages, as well as a growing Beacon state size—our archival Lighthouse node takes up over 16TB! While the volume of messages and the rate of growth in the Beacon state could be diminished by increasing the maximum effective balance, which is currently 32 ETH (and indeed there is talk about an EIP that will serve this purpose), the introduction of such a change would necessitate a delicate balancing act. It would need to ensure that the network remains accessible to individual validators while optimizing for scalability and efficiency.
Source: Coin Metrics Network Data Pro
EIP-7044: Perpetually Valid Signed Voluntary Exits
The introduction of perpetually valid signed voluntary exits allow simpler staking operation designs, enhancing user experience and security of staking operators.
EIP-7045: Increase Max Attestation Inclusion Slot
EIP-7045 proposes increasing the maximum attestation inclusion slot in Ethereum’s blockchain. This change extends the inclusion slot from attestation.slot + SLOTS_PER_EPOCH to the last slot of epoch N+1, where N is the epoch containing the attestation slot. This proposal is a crucial change for the security of LMD-GHOST and enables faster block confirmations, with a new quick confirmation rule free of negative security impacts.
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is the beating heart of Ethereum’s applications. Its language and features allows developers to create safe and gas-efficient contracts, but as any language it too needs to evolve as pain points are identified and dealt with. Many of the upgrades below will help simplify applications running on the EVM reduce costs, and enhance the developer and user experience in the Ethereum network.
The introduction of EIP-1153’s transient storage opcodes and EIP-5656’s MCOPY instruction are technical advances that promise to optimize smart contract interactions and reduce the gas costs associated with complex operations. Meanwhile, EIP-6780’s modification of the SELFDESTRUCT opcode reflects a thoughtful response to the evolving blockchain architecture, addressing issues with state changes and aligning with future architectural changes like Verkle trees.
EIP-7516 adds a new opcode (BLOBBASEFEE) for accessing the blob base-fee, facilitating the trustless passthrough of L1 costs to rollup users based on a price that is enshrined on-chain. Additionally, it permits the creation of derivatives like futures, options, and swaps based on the blob fees.
The Dencun upgrade represents a monumental shift in Ethereum’s evolution, addressing both immediate and long-term scalability, security, and efficiency concerns. With the activation on testnets demonstrating promising results, the Ethereum community is looking forward with anticipation to the mainnet launch. The proposed EIPs, particularly those aimed at optimizing data availability and staking operations, stand to significantly enhance the network’s performance and user experience. As the landscape of Ethereum continues to evolve, it is critical for stakeholders, from validators to end-users, to stay informed and adapt to these changes. Coin Metrics remains committed to providing you with the most up-to-date and comprehensive data-driven insights to navigate this evolving terrain. The progress of the Dencun upgrade and its implications for the broader Ethereum ecosystem will undoubtedly be a focal point in our forthcoming issues.
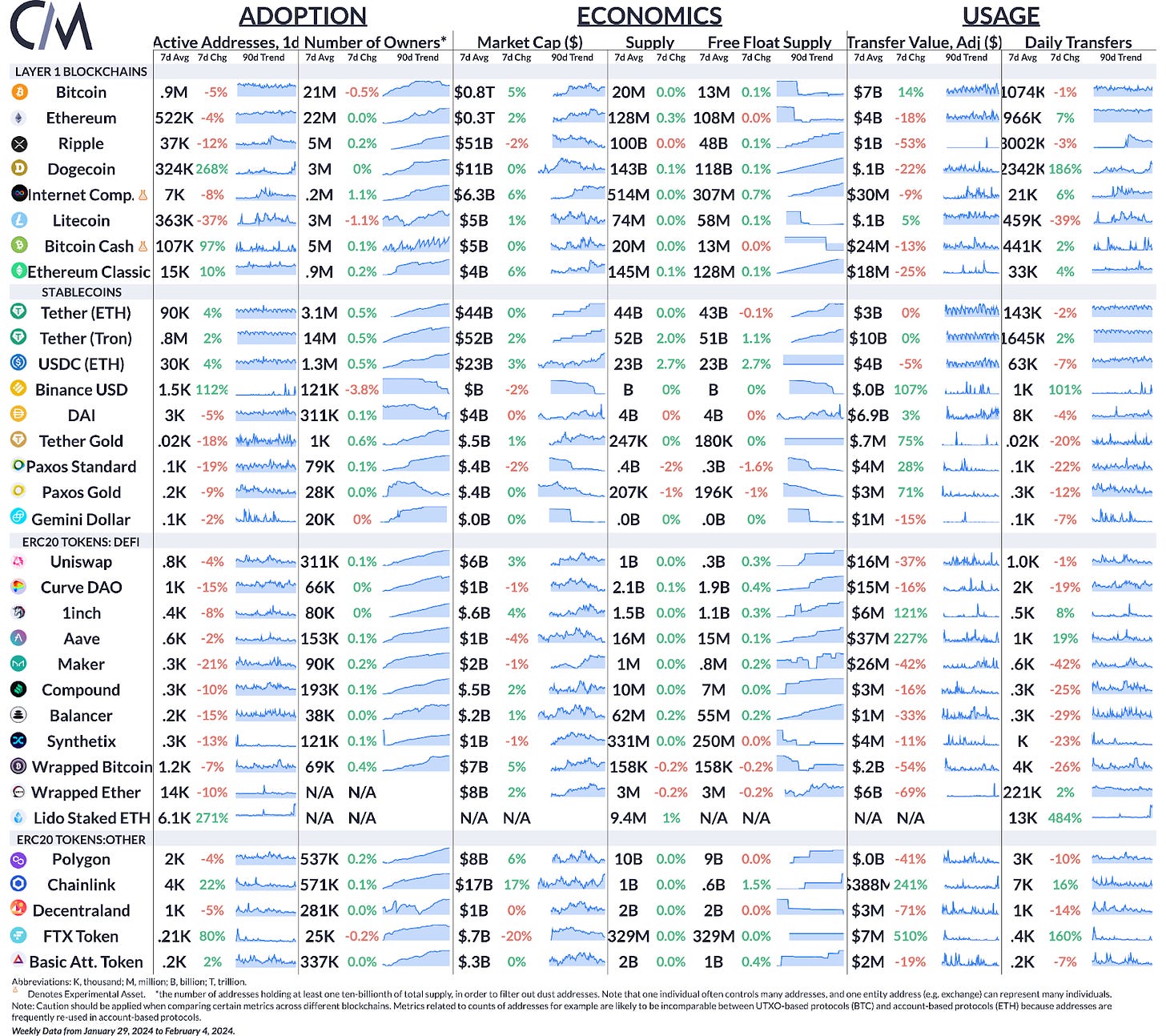
Bitcoin and Ethereum have seen a decrease in active addresses by 5% and 4% respectively over the last week, although the number of owners has remained relatively stable. Network activity across the board appears to slow down after eventful weeks following the bitcoin spot ETF launch.
As always, if you have any feedback or requests please let us know here.
Coin Metrics’ State of the Network, is an unbiased, weekly view of the crypto market informed by our own network (on-chain) and market data.
If you’d like to get State of the Network in your inbox, please subscribe here. You can see previous issues of State of the Network here.
© 2024 Coin Metrics Inc. All rights reserved. Redistribution is not permitted without consent. This newsletter does not constitute investment advice and is for informational purposes only and you should not make an investment decision on the basis of this information. The newsletter is provided “as is” and Coin Metrics will not be liable for any loss or damage resulting from information obtained from the newsletter.
[ad_2]
Read More: coinmetrics.substack.com












 Bitcoin
Bitcoin  Ethereum
Ethereum  Tether
Tether  XRP
XRP  Solana
Solana  USDC
USDC  TRON
TRON  Dogecoin
Dogecoin  Lido Staked Ether
Lido Staked Ether  Cardano
Cardano  Wrapped Bitcoin
Wrapped Bitcoin  Hyperliquid
Hyperliquid  Wrapped stETH
Wrapped stETH  Sui
Sui  Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash  Chainlink
Chainlink  LEO Token
LEO Token  Stellar
Stellar  Avalanche
Avalanche  USDS
USDS  Toncoin
Toncoin  WhiteBIT Coin
WhiteBIT Coin  Shiba Inu
Shiba Inu  Hedera
Hedera  Litecoin
Litecoin  WETH
WETH  Binance Bridged USDT (BNB Smart Chain)
Binance Bridged USDT (BNB Smart Chain)  Wrapped eETH
Wrapped eETH  Monero
Monero  Ethena USDe
Ethena USDe  Polkadot
Polkadot  Bitget Token
Bitget Token  Coinbase Wrapped BTC
Coinbase Wrapped BTC  Pepe
Pepe  Uniswap
Uniswap  Pi Network
Pi Network  Aave
Aave  Dai
Dai  Ethena Staked USDe
Ethena Staked USDe  OKB
OKB  Bittensor
Bittensor  BlackRock USD Institutional Digital Liquidity Fund
BlackRock USD Institutional Digital Liquidity Fund  Aptos
Aptos  sUSDS
sUSDS  Cronos
Cronos  Internet Computer
Internet Computer  NEAR Protocol
NEAR Protocol  Jito Staked SOL
Jito Staked SOL  Ethereum Classic
Ethereum Classic