“Don’t put all your eggs in one basket” — this saying rings true for any market, especially the cryptocurrency market, where volatility is a significant concern.
The crypto ecosystem offers various investment opportunities; however, investing in this rapidly evolving asset class can be risky. Investing all your capital into a single asset can be an even riskier proposition, akin to putting all your eggs in one basket. That’s where portfolio diversification strategies come in. Crypto portfolio diversification means spreading investments across different cryptocurrencies to reduce exposure to any single asset or market risk. Rather than relying on a single asset to generate returns, diversification allows you to spread your investment across different safety nets and potentially reap the benefits of a more resilient and well-diversified portfolio.
In this article, we’ll explore the different crypto portfolio diversification strategies investors can adopt to build a well-rounded and resilient cryptocurrency portfolio to mitigate risks and maximize returns. Ready? Let’s start the journey.
Why Is Crypto Portfolio Diversification Important?
Crypto portfolio diversification is an essential strategy for managing the inherent volatility and uncertainty of the crypto market.
The high volatility and unpredictability of the market can cause a crypto asset to experience extreme price fluctuations in a short period. Diversifying your investment portfolio across different crypto assets allows you to mitigate the risk of investing in any particular asset that may experience a sudden drop in value due to unforeseen circumstances.
Diversification can also help capture potential gains from different industries and underlying asset classes. By spreading investments across multiple coins with different use cases, market segments, and technological advancements, crypto investors can benefit from the growth potential of various sectors of the crypto market.
This can help create a well-balanced portfolio, providing a cushion against the volatile market and enhancing long-term profitability.
Overview of Crypto Portfolio Diversification Strategies
Let’s look closer into various cryptocurrency diversification strategies a crypto investor can apply to create an ideal portfolio.
Risk-Based Diversification
Risk-based diversification, RBD, involves spreading your crypto investments across different coins based on their risk levels. Generally, high-risk investments have the potential for greater returns. By diversifying your crypto holdings across cryptocurrencies with varying degrees of risk, you can create a balanced portfolio that aligns with your risk tolerance.
An RBD portfolio might comprise such coins as:
- Bitcoin (low-risk, low volatility, high liquidity)
- Ethereum (higher-risk, high volatility, high liquidity)
- Binance Coin (mid-risk, moderate volatility, and liquidity)
- Chainlink (higher-risk, high volatility, lower liquidity)
- Uniswap (higher-risk, high volatility, moderate liquidity)
- USD Coin (low-risk, high liquidity, stable)
- Solana (higher-risk, high volatility, moderate liquidity).
Sector-Focused Diversification
Sector-focused diversification, SFD, involves spreading your cryptocurrency investments across different assets from multiple crypto sectors. For example, you might diversify your crypto portfolio by allocating funds to payment coins, security tokens, governance tokens, and other assets involved with supply chains, smart contracts, gaming, decentralized Finance (DeFi), or non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Investing in crypto projects from different sectors helps you create a well-balanced portfolio management strategy to capture potential gains from different trends and developments in the crypto economy.
Here’s what an SFD portfolio might look like:
- DeFi (Decentralized Finance) Sector: Aave (AAVE), Compound (COMP), and Maker (MKR)
- NFT (Non-Fungible Token) Sector: Enjin Coin (ENJ), Flow (FLOW), and Chiliz (CHZ)
- Gaming Sector: Theta Token (THETA), Axie Infinity (AXS), and Decentraland (MANA)
- Infrastructure Sector: Polkadot (DOT), Cardano (ADA), and Chainlink (LINK).
Thematic Diversification
Thematic diversification, TD, involves investing in cryptocurrencies based on a specific theme or idea. For example, you might invest in cryptocurrencies focused on privacy, sustainability, or social impact. Investing in cryptocurrencies that align with your values or interests can create a portfolio that reflects your personal beliefs and goals.
Here are some examples of TD portfolios:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi) theme: Ethereum (ETH), Uniswap (UNI), Aave (AAVE), Compound (COMP)
- Privacy and anonymity theme: Monero (XMR), Zcash (ZEC), Dash (DASH), Pirate Chain (ARRR)
- Energy-efficient theme: Chia (XCH), Cardano (ADA), Ethereum (ETH), Solana (SOL).
- Gaming and NFT theme: Axie Infinity (AXS), Enjin Coin (ENJ), Decentraland (MANA), The Sandbox (SAND)
- Internet of Things (IoT) theme: IOTA (MIOTA), VeChain (VET), Waltonchain (WTC), Helium (HNT)
- Web 3.0 theme: Polkadot (DOT), Chainlink (LINK), Filecoin (FIL), Arweave (AR), The Graph (GRT).
Market Cap-Based Diversification
Market cap-based diversification, MCBD, involves crypto investing based on cryptocurrencies’ market capitalization. Cryptocurrencies with larger market capitalizations are typically more established and less volatile than smaller, less-established cryptocurrencies. Investing in cryptocurrencies with different market caps reduces your portfolio’s risk and helps you create a well-balanced crypto portfolio of established cryptocurrencies and potentially high-growth, smaller cryptocurrencies.
Some market-cap-based crypto portfolio examples are described below:
- Large-caps: Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), Binance Coin (BNB)
- Mid-caps: Cardano (ADA), Ripple (XRP), Dogecoin (DOGE), Chainlink (LINK), Solana (SOL), Polkadot (DOT), Polygon (MATIC)
- Small-caps: Serum (SRM), Chiliz (CHZ), Holo (HOT), Helium (HNT), Origin Protocol (OGN), SushiSwap (SUSHI)
Time-Horizon-Based Diversification
Time-horizon-based diversification, THBD, involves investing in cryptocurrencies based on your investment time horizon. Generally, longer investment time horizons allow for greater risk tolerance and potential for higher returns, while shorter time horizons require a more conservative approach with lower-risk investments.
Let’s look at a few examples of a time-horizon-based diversified portfolio:
- Short-term (1-6 months): Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), Binance Coin (BNB), Polkadot (DOT), and Solana (SOL). Investing in these assets provides high returns in a short period but also comes with increased risk.
- Medium-term (6-12 months): Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), Cardano (ADA), Chainlink (LINK), and Uniswap (UNI). This portfolio is less volatile and provides growth opportunities.
- Long-term (12+ months): Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), Polkadot (DOT), Chainlink (LINK), and Cardano (ADA). These coins have strong development teams and solid use cases and are expected to grow in value over the long term.
Types of Cryptocurrencies to Consider for Diversification
Bitcoin
Bitcoin is the world’s first and largest decentralized digital currency. Regarding crypto portfolio diversification, Bitcoin is undoubtedly one of the most popular choices. Most investors widely accept it, and many view it as digital gold or a hedge against inflation. Its liquidity is also very high, allowing you to buy or sell BTC in large quantities easily.
Bitcoin has a limited supply, meaning its value may continue to rise as demand increases. However, its high volatility means it can also experience significant price drops, so managing risk when investing in Bitcoin is essential.
Coins
While Bitcoin is also considered a coin, it deserves a separate section — this one will focus on non-Bitcoin coins.
The multifacetedness of coins makes them attractive investments. Altcoins are generally riskier than Bitcoin, as they often have less established user bases and are subject to higher volatility. However, they also offer a high-risk profile investor the potential for higher returns.
Based on their blockchain solutions, coins are differentiated into Layer 1 and Layer 2 coins.
Layer 1 refers to the base layer of a blockchain network, including the underlying protocol and consensus mechanism. Layer 1 coins are the backbone of their respective blockchain networks and are used to power transactions and execute smart contracts. Examples of Layer 1 coins include Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, and Bitcoin Cash.
Layer 2 refers to the second layer of a blockchain network, built on top of the base layer to improve the functionality and scalability of the underlying blockchain. Layer 2 coins offer additional features such as faster transaction speeds, lower fees, and increased security. Examples of Layer 2 coins include Lightning Network (built on top of Bitcoin’s blockchain), Plasma (built on top of Ethereum’s blockchain), and Raiden Network (built on top of the Ethereum blockchain).
Both Layer 1 and Layer 2 coins are essential components of the cryptocurrency ecosystem, and each serves a unique purpose in supporting the development of the industry.
Tokens
Tokens are cryptocurrencies built atop an existing blockchain, and are not used to pay gas fees on it. Rather, they offer some other form of utility.
Utility tokens are typically issued by blockchain-based companies to incentivize users to participate in the network. Investing in utility tokens can provide exposure to specific blockchain-based services and products. It can also offer the potential for high returns if the underlying product or service gains popularity and adoption.
DeFi projects are designed to provide financial services using blockchain technology, such as lending, borrowing, and trading. Investing in DeFi projects can provide exposure to various financial services unavailable for traditional investments through traditional financial institutions. However, remember that DeFi projects can be highly complex and risky.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
NFTs are unique digital assets stored on the blockchain that cannot be replicated or exchanged for something else. They often represent artwork, collectibles, and in-game items. NFTs offer a new way of investing in the crypto space with the potential for significant growth.
However, investing in NFTs can be highly speculative and volatile. The value of NFTs can fluctuate based on various factors, including the popularity of the underlying digital asset, the rarity of the NFT, and the overall market sentiment.
Stablecoins
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies pegged to a stable fiat currency, such as the US dollar or gold. They provide a hedge against the volatility of the cryptocurrency market and can be used as a means of payment or store of value as they can be exchanged for one or more fiat currencies.
Investing in stablecoins provides a stable and predictable source of income for investors and reduces the volatility of a crypto portfolio.
However, investing in stablecoins doesn’t provide the same potential for high returns as other cryptocurrencies due to their stable value.
Real-World Crypto Portfolio Examples
Crypto portfolios can be categorized into three broad categories: conservative, balanced, and aggressive. Each type represents a specific level of risk and potential return. Let’s consider each category with examples.
Conservative Crypto Portfolio
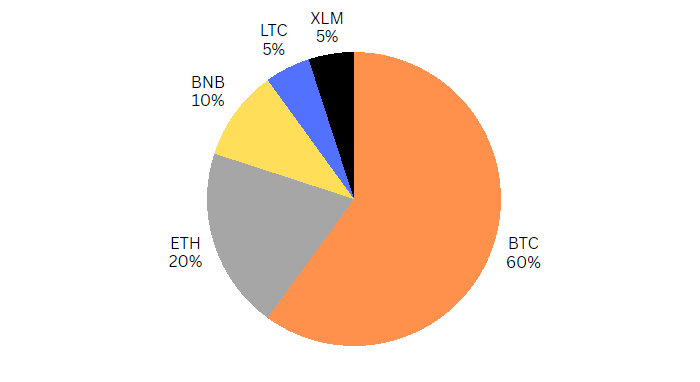
Conservative portfolios focus on low-risk, stable investments with steady returns. These portfolios are generally geared toward investors looking for long-term investment stability. Conservative portfolios usually consist of large-cap, established cryptocurrencies with low volatility. Let’s look at an example of a conservative crypto portfolio:
Example
- Bitcoin (BTC) – 60%
- Ethereum (ETH) – 20%
- Binance Coin (BNB) – 10%
- Litecoin (LTC) – 5%
- Stellar (XLM) – 5%
Balanced Crypto Portfolio
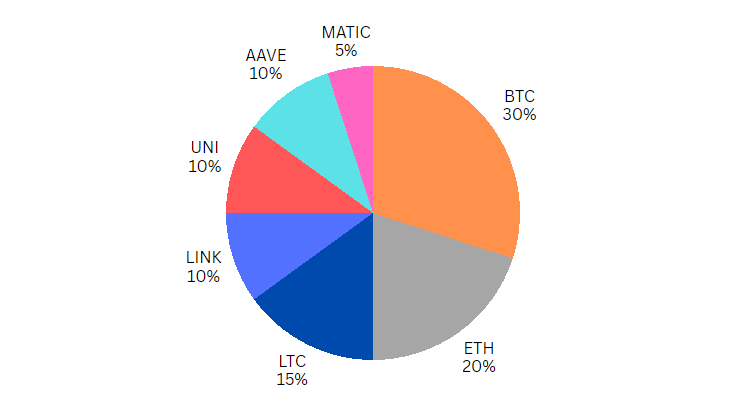
Balanced portfolios aim to balance risk and reward by investing in a mix of low and high-risk assets. This type of portfolio is suitable for investors who want to strike a balance between long-term stability and short-term growth potential. Balanced portfolios usually consist of a mix of established cryptocurrencies and emerging altcoins.
Let’s consider an example of a balanced crypto portfolio:
Example
- Bitcoin (BTC) – 30%
- Ethereum (ETH) – 20%
- Litecoin (LTC) – 15%
- Chainlink (LINK) – 10%
- Uniswap (UNI) – 10%
- Aave (AAVE) – 10%
- Polygon (MATIC) – 5%
Aggressive Crypto Portfolio
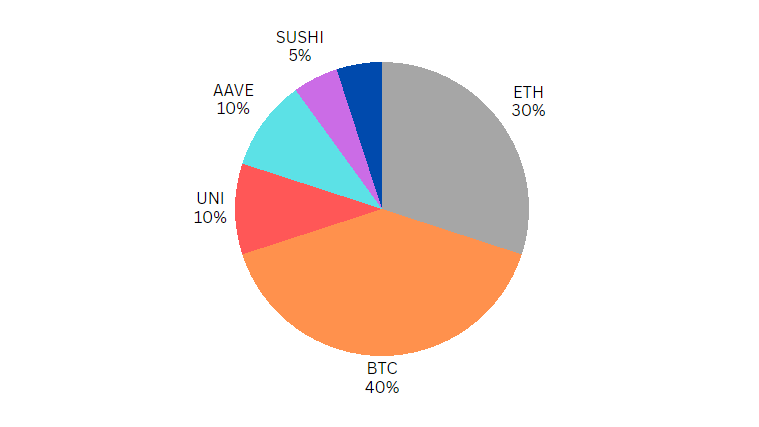
An aggressive crypto portfolio comprises mostly small-cap crypto assets with higher risk and growth potential. This portfolio aims to maximize returns in the short term, with high exposure to market volatility. Aggressive investors may also consider investing in new, emerging cryptocurrencies, ICOs (Initial Coin Offerings), or DeFi (Decentralized Finance) projects. Let’s look at an example of an aggressive crypto portfolio:
Example
- Ethereum (ETH) – 40%
- Bitcoin (BTC) – 30%
- Uniswap (UNI) – 10%
- Aave (AAVE) – 10%
- Ankr (ANKR) – 5%
- Sushi (SUSHI) – 5%
Conclusion
Diversification is crucial in building a successful crypto portfolio. Investors can reduce the risks of a market downturn and increase potential returns by spreading investments across different cryptocurrencies, market cap categories, exchanges, investment strategies, stablecoins, and geographical regions. Regularly monitoring and rebalancing the portfolio is also essential to ensure the portfolio stays aligned with investment goals and market conditions.
However, while diversification can help mitigate risks, it can’t guarantee profits 100% of the time or protect against losses completely. Crypto is considered a high-risk investment, and investors are advised to conduct their own research, understand the risks involved, and only risk the amount of money they can afford to lose.
Disclaimer: All information provided in or through the CoinStats Website is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute a recommendation to enter into a particular transaction or investment strategy and should not be relied upon in making an investment decision. Any investment decision made by you is entirely at your own risk. In no event shall CoinStats be liable for any incurred losses. See our Disclaimer and Editorial Guidelines to learn more.
Read More: coinstats.app









 Bitcoin
Bitcoin  Ethereum
Ethereum  Tether
Tether  XRP
XRP  Solana
Solana  USDC
USDC  Dogecoin
Dogecoin  TRON
TRON  Cardano
Cardano  Lido Staked Ether
Lido Staked Ether  Wrapped Bitcoin
Wrapped Bitcoin  Hyperliquid
Hyperliquid  Wrapped stETH
Wrapped stETH  Sui
Sui  Chainlink
Chainlink  LEO Token
LEO Token  Stellar
Stellar  Avalanche
Avalanche  Toncoin
Toncoin  Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash  Shiba Inu
Shiba Inu  USDS
USDS  Hedera
Hedera  WETH
WETH  Litecoin
Litecoin  Wrapped eETH
Wrapped eETH  Monero
Monero  Binance Bridged USDT (BNB Smart Chain)
Binance Bridged USDT (BNB Smart Chain)  Polkadot
Polkadot  Ethena USDe
Ethena USDe  Bitget Token
Bitget Token  Pepe
Pepe  Coinbase Wrapped BTC
Coinbase Wrapped BTC  Pi Network
Pi Network  WhiteBIT Coin
WhiteBIT Coin  Aave
Aave  Uniswap
Uniswap  Dai
Dai  Ethena Staked USDe
Ethena Staked USDe  Bittensor
Bittensor  OKB
OKB  Cronos
Cronos  BlackRock USD Institutional Digital Liquidity Fund
BlackRock USD Institutional Digital Liquidity Fund  Aptos
Aptos  NEAR Protocol
NEAR Protocol  Jito Staked SOL
Jito Staked SOL  Internet Computer
Internet Computer  Ondo
Ondo  Ethereum Classic
Ethereum Classic