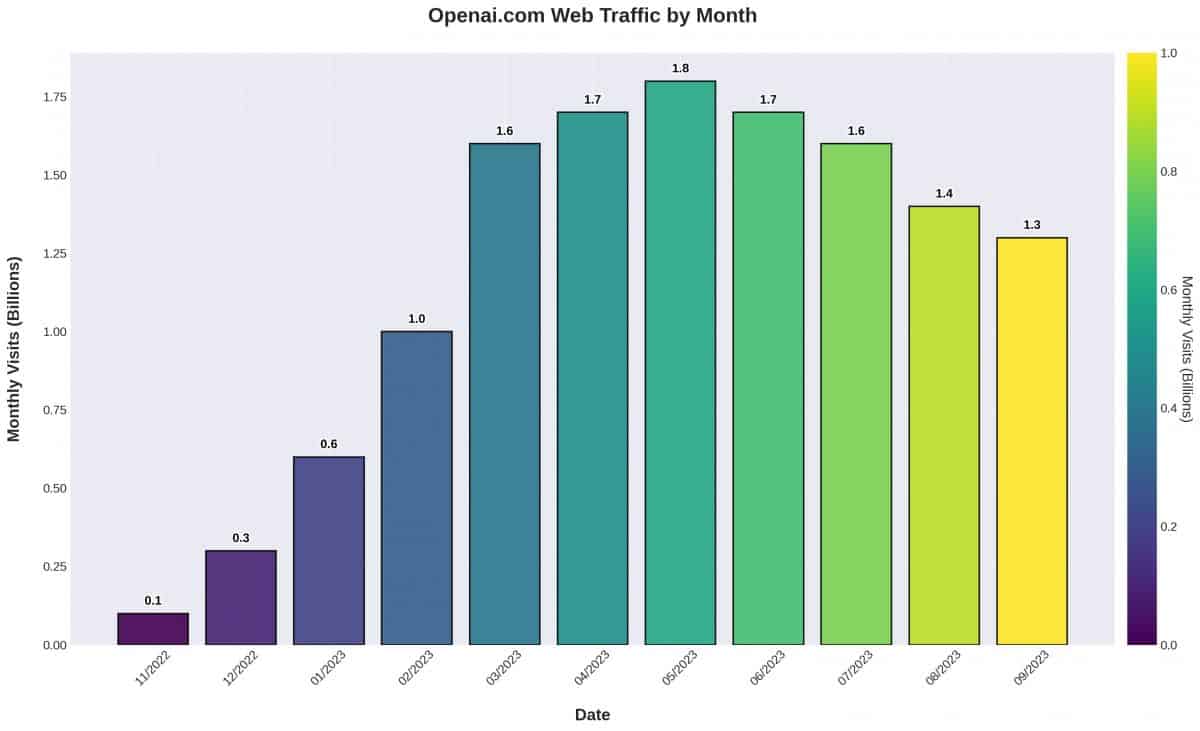
In November 2022, OpenAI launched ChatGPT, a conversational large language model that quickly took the world by storm. From its inception to its peak in May, the website saw unprecedented growth, becoming what some analysts called “the fastest-growing web app in internet history.” However, recent data indicates a decline in traffic and engagement.
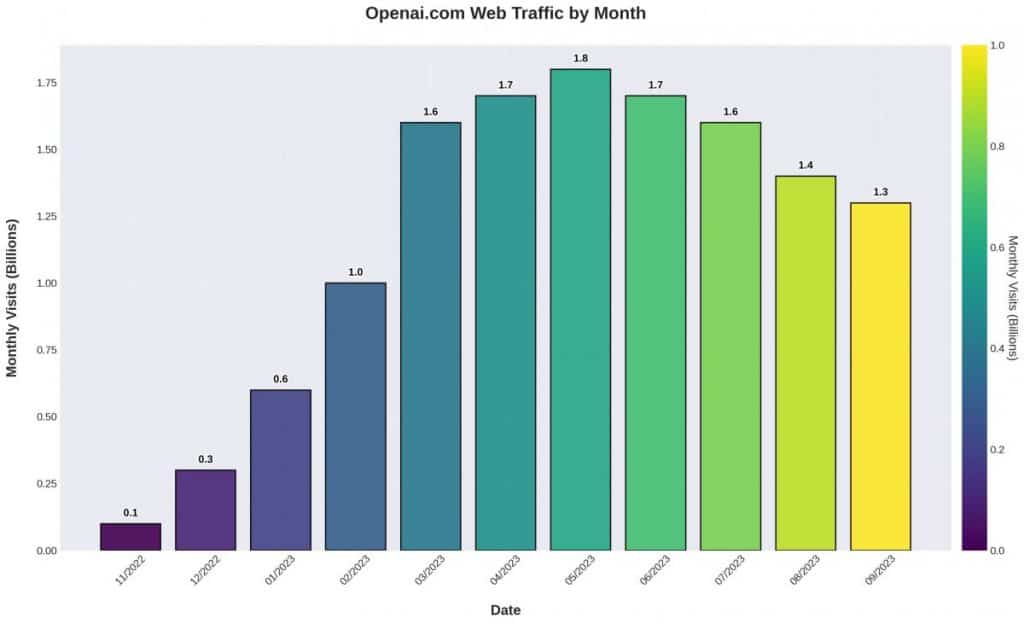
According to data from Similarweb, by January 2023, ChatGPT had attracted a staggering 100 million monthly active users. Its appeal lay in its capability, accessibility, and the fact that it was free. Users from all over the globe flocked to the platform to generate a variety of text outputs, from emails and essays to code snippets.
ChatGPT wasn’t just a tool; it was a sensation that contributed significantly to the AI hype. Its advanced natural language processing capabilities enabled it to perform a wide range of tasks, including question-answering and text summarization. This versatility led to a surge in chatbot applications and placed generative AI on the map in an unprecedented way.
However, all that glitters is not gold. Data from June revealed that global traffic to ChatGPT dropped by 9.7%, with a 10.3% decline in the U.S. alone. Unique visitor numbers fell by 5.7%, and user engagement dipped by 8.5% compared to May. This marks the first significant decline since the website’s launch.
One plausible explanation for the drop in usage could be the closing of schools for the summer. ChatGPT was popular for answering homework questions, and with students turning their attention to other activities like Minecraft, this could account for some of the decline.
Another possibility is that users are becoming more efficient in their interactions with the bot. Rather than spending time exploring its capabilities, they might be using it for more specific tasks, thereby reducing overall engagement time.
OpenAI offers its models via APIs and Microsoft Azure. The decline in website traffic might be attributed to users transitioning to these programmatic interfaces for more tailored uses.
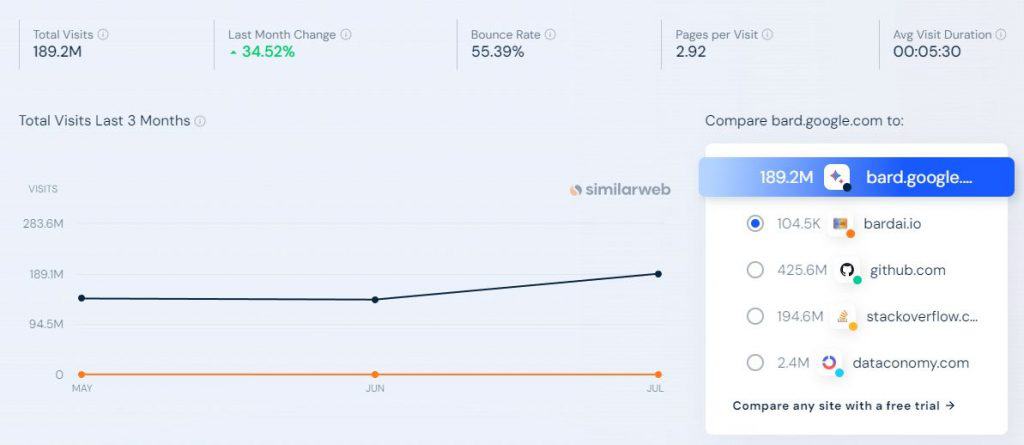
ChatGPT’s decline comes amidst a broader context of market dynamics. For instance, Character.AI, another popular AI chatbot site, saw a 32% decline in traffic. Meanwhile, Google’s Bard is slowly gaining traction.
OpenAI has announced that its latest models, including GPT-4, are now generally available for API access. Older models based on GPT-3 will be retired by January 4, 2024, and replaced with newer systems. This could potentially rejuvenate interest and bring back some of the lost traffic.
The decline in ChatGPT’s web traffic doesn’t necessarily spell doom for the platform or for AI-powered chatbots in general. It might simply be a market correction, a seasonal fluctuation, or a sign of users becoming more focused in their interactions.
Would you like to discuss the article or have any other queries? Feel free to ask!
Read more about AI:
Read More: mpost.io








 Bitcoin
Bitcoin  Ethereum
Ethereum  Tether
Tether  XRP
XRP  Solana
Solana  USDC
USDC  Dogecoin
Dogecoin  Cardano
Cardano  TRON
TRON  Lido Staked Ether
Lido Staked Ether  Wrapped Bitcoin
Wrapped Bitcoin  Sui
Sui  Wrapped stETH
Wrapped stETH  Chainlink
Chainlink  Avalanche
Avalanche  Hyperliquid
Hyperliquid  Stellar
Stellar  Shiba Inu
Shiba Inu  Hedera
Hedera  Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash  LEO Token
LEO Token  Toncoin
Toncoin  Litecoin
Litecoin  Polkadot
Polkadot  Monero
Monero  WETH
WETH  USDS
USDS  Wrapped eETH
Wrapped eETH  Bitget Token
Bitget Token  Pepe
Pepe  Pi Network
Pi Network  Binance Bridged USDT (BNB Smart Chain)
Binance Bridged USDT (BNB Smart Chain)  Ethena USDe
Ethena USDe  Coinbase Wrapped BTC
Coinbase Wrapped BTC  WhiteBIT Coin
WhiteBIT Coin  Bittensor
Bittensor  Aave
Aave  Uniswap
Uniswap  Dai
Dai  NEAR Protocol
NEAR Protocol  Aptos
Aptos  Jito Staked SOL
Jito Staked SOL  OKB
OKB  Ondo
Ondo  Cronos
Cronos  Ethereum Classic
Ethereum Classic  Internet Computer
Internet Computer  BlackRock USD Institutional Digital Liquidity Fund
BlackRock USD Institutional Digital Liquidity Fund