[ad_1]
Blockchain technology is a decentralized and distributed ledger that enables secure, transparent, and immutable transactions. It operates through a network of computers that validate and record each transaction in a series of blocks, which are linked and encrypted to form a chain. This technology has become increasingly popular in recent years, with the rise of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
However, blockchain technology is more than just a digital currency. It has several layers that enable its functionality and performance. Understanding these layers is essential for businesses and investors who want to leverage blockchain technology for their operations or investments.
The Layers of Blockchain
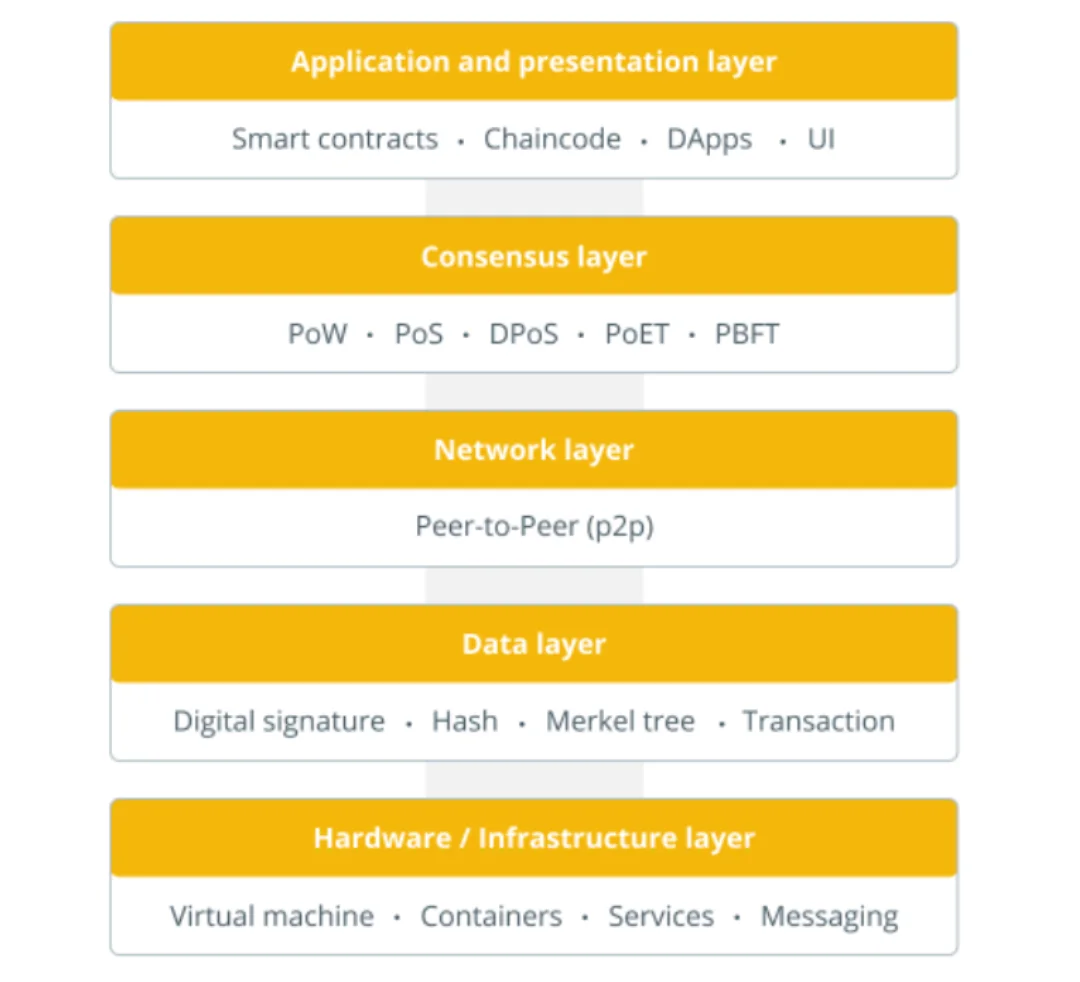
A typical blockchain system consists of several layers that work together to ensure the integrity and efficiency of transactions. These layers include:
- Network Layer: This layer includes the physical network of computers and nodes that communicate with each other to form the blockchain network. It is responsible for connecting nodes, propagating transactions, and distributing data across the network.
- Consensus Layer: This layer ensures that all nodes in the network agree on the validity of each transaction. It relies on a consensus mechanism, such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain.
- Data Layer: This layer stores all transaction data in a secure and immutable manner. It includes the transaction ledger, which contains all the transactions in the blockchain, and the state database, which stores the current state of the blockchain.
- Application Layer: This layer includes the smart contracts, decentralized applications (dApps), and other software that run on top of the blockchain network. It enables developers to build new applications and services that leverage the blockchain’s security and transparency.
- Hardware Layer: This layer includes the physical devices, such as computers and servers, that support the blockchain network. It includes the hardware infrastructure, such as mining equipment, that is used to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain.
Each layer in the blockchain system plays a critical role in ensuring the security, transparency, and efficiency of transactions. In the following sections, we will explore each layer in more detail and its importance for blockchain technology.
The Importance of Blockchain Scalability
One of the biggest challenges facing blockchain technology is scalability. As more users and transactions are added to the blockchain network, the system becomes slower and less efficient. This is because the current blockchain architecture cannot support the increased demand for transaction processing.
To address this issue, several solutions have been proposed, including:
- Layer 1 vs. Layer 2 Blockchain: Layer 1 refers to the base layer of the blockchain, where all transactions are recorded and validated. Layer 2 refers to a secondary layer built on top of Layer 1 that can handle more transactions and improve the blockchain’s scalability. Layer 2 solutions include sidechains, state channels, and payment channels.
- Consensus Mechanism: The consensus mechanism used by the blockchain network can also affect its scalability. Proof of Work (PoW) is the most widely used consensus mechanism in blockchain, but it is slow and energy-intensive. Proof of Stake (PoS) is a more efficient consensus mechanism that can improve blockchain scalability.
- Blockchain Architecture: The blockchain architecture can also affect its scalability. A sharded blockchain architecture, for example, can divide the blockchain network into smaller groups of nodes, each responsible for processing a subset of transactions. This can improve the blockchain’s scalability by reducing the load on each node.
- Distributed Ledger Technology: Distributed ledger technology (DLT) is a type of blockchain technology that can improve scalability by enabling multiple nodes to process transactions simultaneously. This can improve the speed and efficiency of transaction processing, making the blockchain more scalable.
The Six Layers of Blockchain
In addition to the five layers described earlier, some blockchain experts have proposed an additional layer, Layer 0, which refers to the underlying protocols and standards that govern the blockchain network. This layer includes protocols such as TCP/IP, HTTP, and SSL, which enable communication and security on the blockchain network.
The six layers of blockchain are:
- Layer 0: The underlying protocols and standards that govern the blockchain network.
- Layer 1: The network layer, which includes the physical network of computers and nodes that communicate with each other to form the blockchain network.
- Layer 2: The consensus layer, which ensures that all nodes in the network agree on the validity of each transaction.
- Layer 3: The data layer, which stores all transaction data in a secure and immutable manner.
- Layer 4: The application layer, which includes the smart contracts, dApps, and other software that run on top of the blockchain network.
- Layer 5: The user layer, which includes the end-users who interact with the blockchain network through wallets, browsers, and other applications.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize industries and transform the way we conduct transactions. Understanding its layers and scalability is essential for businesses and investors who want to leverage this technology’s benefits. By addressing the scalability issue and improving the blockchain architecture, we can unlock its full potential and create a more secure, transparent, and efficient digital economy.
[ad_2]
Read More: coinstats.app









 Bitcoin
Bitcoin  Ethereum
Ethereum  Tether
Tether  XRP
XRP  Solana
Solana  USDC
USDC  TRON
TRON  Dogecoin
Dogecoin  Lido Staked Ether
Lido Staked Ether  Cardano
Cardano  Wrapped Bitcoin
Wrapped Bitcoin  Hyperliquid
Hyperliquid  Wrapped stETH
Wrapped stETH  Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash  Sui
Sui  LEO Token
LEO Token  Chainlink
Chainlink  USDS
USDS  Stellar
Stellar  Avalanche
Avalanche  Toncoin
Toncoin  WhiteBIT Coin
WhiteBIT Coin  Shiba Inu
Shiba Inu  Binance Bridged USDT (BNB Smart Chain)
Binance Bridged USDT (BNB Smart Chain)  Litecoin
Litecoin  WETH
WETH  Wrapped eETH
Wrapped eETH  Hedera
Hedera  Ethena USDe
Ethena USDe  Monero
Monero  Polkadot
Polkadot  Coinbase Wrapped BTC
Coinbase Wrapped BTC  Bitget Token
Bitget Token  Pi Network
Pi Network  Pepe
Pepe  Uniswap
Uniswap  Dai
Dai  Aave
Aave  Ethena Staked USDe
Ethena Staked USDe  OKB
OKB  BlackRock USD Institutional Digital Liquidity Fund
BlackRock USD Institutional Digital Liquidity Fund  Bittensor
Bittensor  Aptos
Aptos  sUSDS
sUSDS  Cronos
Cronos  Internet Computer
Internet Computer  Jito Staked SOL
Jito Staked SOL  NEAR Protocol
NEAR Protocol  Ethereum Classic
Ethereum Classic