The issue of regulation within the world of blockchain technology is unlikely to be resolved any time soon. Despite widespread cryptocurrency market downturns throughout 2022, $3 billion in crypto assets were stolen by hackers across the year, the highest total ever recorded for digital asset heists. This apparent lack of security has brought regulated and unregulated blockchains into the spotlight. So, what’s the difference? And can true decentralization be achieved alongside regulation?
How a Blockchain Works
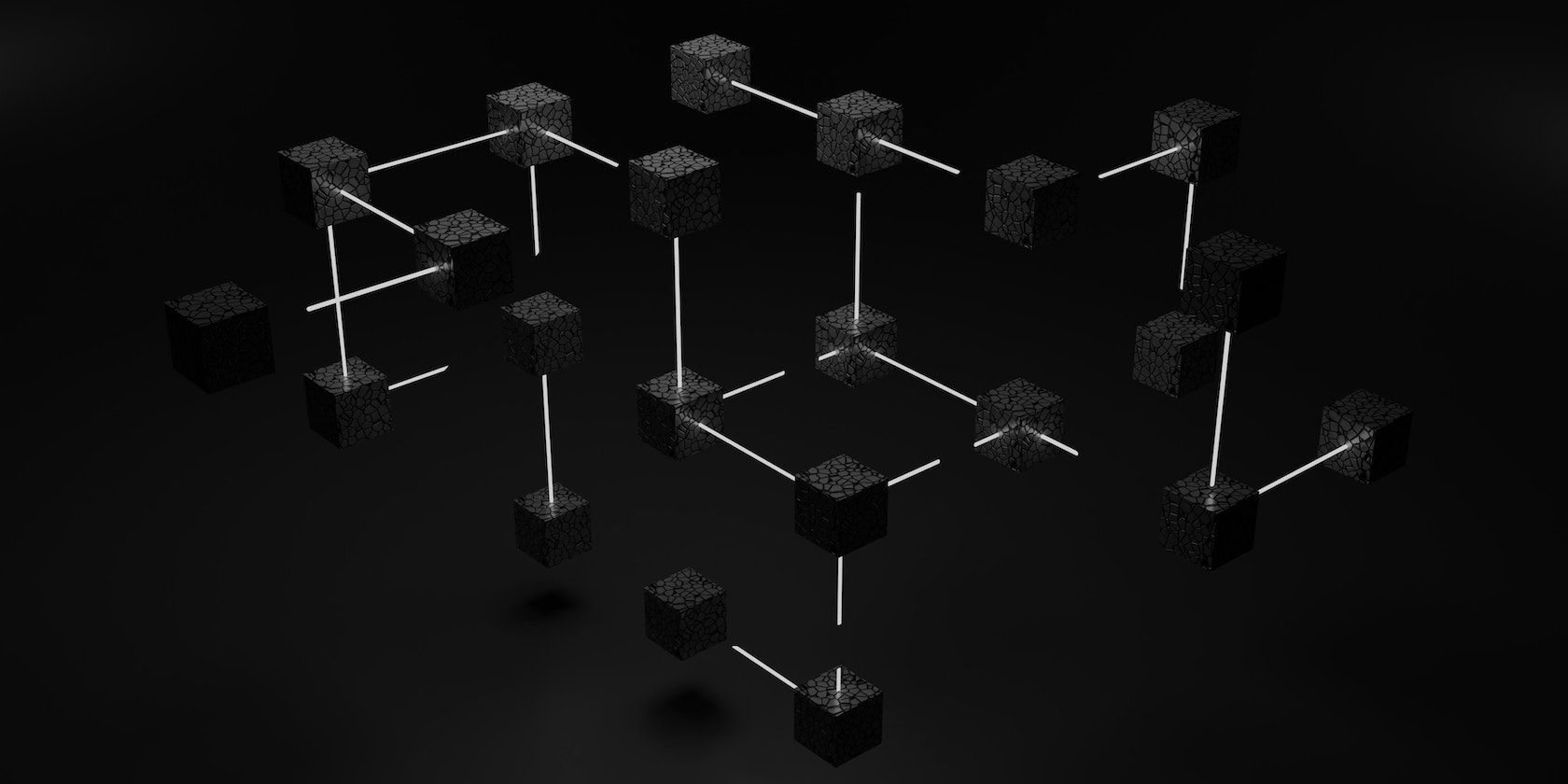
One of the greatest perks of the blockchain landscape is decentralization. The revolutionary technology, which is made secure through an interconnected collection of distributed computers, means that there is no single central owner. When it comes to a blockchain, any changes must be agreed upon by a predetermined number of distributed computers, or “nodes,” to alter or add to the information stored.
While this procedure may seem complex, blockchains can broker transactions in a matter of seconds. Moreover, because of how profoundly difficult it can be for a hacker to gain access to a sufficient number of globally distributed computers, it’s virtually impossible for a blockchain to be compromised.
So why are thieves still stealing record-breaking volumes of crypto and blockchain assets like NFTs? The answer is that many cybercriminals have taken aim at phishing and tricking asset holders into willfully handing over their valuable goods in scams.
In March 2022, the European Union called for cryptocurrency transfers to be made fully traceable to ensure that any illegal activity could be better monitored. Introduced as part of the EU’s anti-money laundering package, the move would introduce a considerable amount of regulation into the blockchain ecosystem but would fly in the face of a truly decentralized landscape.
Today, we can see examples of both regulated and unregulated blockchains populating the ecosystem, with both carrying different perks for users. Let’s take a deeper look at the key differences between both regulated and unregulated blockchains:
What Are Regulated Blockchains?
Regulated blockchains are rarer to find and are generally centralized in nature. Because of this, they’re usually termed as “private” blockchains, where a single organization has authority over a network.
While this means that regulated blockchains can technically afford more privacy, particularly for enterprises seeking to bring more efficiency to their internal processes, many people believe that its centralized nature means that governing authorities could bend the rules and override transactions. This prospect can be significantly off-putting for cryptocurrency enthusiasts.
Despite this, regulated blockchains can carry plenty of useful perks. Their centralized nature makes regulated blockchains generally faster than their decentralized counterparts and can be significantly more stable than more distributed public blockchains.
Above all, regulated blockchains make it harder for illegal activity to take place, at least from hackers and other criminals. These centralized chains can even add an authentication process before users can access the network.
Furthermore, their regulatory framework means that suspicious activity can be quickly identified and addressed, with less risk for users and their assets.
However, handing centralized control of a blockchain over to a single organization or entity means that users are placing their trust in the owner of the chain. This means that, unlike fully distributed and decentralized systems, your information is never fully private.
What Are Unregulated Blockchains?
Unregulated blockchains heavily populate the cryptocurrency ecosystem and allow users to join whenever they want. Here, users have no restrictions, and participation in the consensus process is open to everyone.
Today’s leading cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, operate on unregulated blockchains. The latter’s chain currently hosts the world’s largest array of decentralized finance applications and platforms that millions of users enjoy.
These unregulated blockchains are also known as “public” blockchains because they are largely completely decentralized. It means that no single entity controls the chain, which theoretically empowers all users to have full control over their assets, information, and transactions.
While regulated blockchains can be great for mitigating instances of illegal activity, there’s little doubt that the security offered by unregulated blockchains is exceptional and unparalleled in any digital landscape.
Because all changes and transactions made within the chain need to be verified across a vast decentralized network of nodes, breaking into a public blockchain is virtually impossible for cybercriminals (an attacker would need to control 51 percent of the network), but a lack of regulation means that scammers face few consequences should they trick you into handing over your credentials or assets. In short, once your crypto is gone, it isn’t coming back.
Additionally, because it’s a public ledger, unregulated blockchains are transparent at all times, meaning that all participants can view all activity recorded on the blockchain, offering more security against corrupt activities. However, the anonymity aspect of unregulated blockchains means that users can still make transactions for just about any means as they see fit. While this is a great way to preserve privacy, it can also lead to more underhanded transactions taking place on the ledger.
Can Public Blockchains Ever be Regulated?
Although governmental bodies like the European Union and SEC have long sought to bring regulation to blockchain technology, successful regulation is only possible through finding some form of coexistence alongside a fully decentralized and open system.
The biggest supporters of blockchain remain adamant that full decentralization must be preserved at all times and that the technology can have designers buy no owners under any circumstances.
Because data is freely dispersed across the network, it’s certainly possible for decentralization and regulation to coexist, and encryption schemes could seek to ensure that predetermined users can view certain data without larger centralized bodies interrupting the fabric of a functional blockchain.
Looking to Blockchain’s Role in the Future
As the age of Web3 continues to provide us with more hints as to how blockchain technology can deliver a future of intelligent transactions and online privacy, we’re likely to see more interpretations of distributed ledgers emerge.
Taking its role as the more powerful and immutable solution to data security available today, it’s probable that the next generation of the internet will be built on blockchain.
Read More: news.google.com









 Bitcoin
Bitcoin  Ethereum
Ethereum  Tether
Tether  XRP
XRP  Solana
Solana  USDC
USDC  Dogecoin
Dogecoin  TRON
TRON  Cardano
Cardano  Lido Staked Ether
Lido Staked Ether  Wrapped Bitcoin
Wrapped Bitcoin  Hyperliquid
Hyperliquid  Sui
Sui  Wrapped stETH
Wrapped stETH  Chainlink
Chainlink  Avalanche
Avalanche  LEO Token
LEO Token  Stellar
Stellar  Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash  Toncoin
Toncoin  Shiba Inu
Shiba Inu  Hedera
Hedera  USDS
USDS  Litecoin
Litecoin  WETH
WETH  Wrapped eETH
Wrapped eETH  Polkadot
Polkadot  Monero
Monero  Binance Bridged USDT (BNB Smart Chain)
Binance Bridged USDT (BNB Smart Chain)  Ethena USDe
Ethena USDe  Bitget Token
Bitget Token  Pepe
Pepe  Coinbase Wrapped BTC
Coinbase Wrapped BTC  Pi Network
Pi Network  WhiteBIT Coin
WhiteBIT Coin  Aave
Aave  Uniswap
Uniswap  Dai
Dai  Bittensor
Bittensor  Ethena Staked USDe
Ethena Staked USDe  Internet Computer
Internet Computer  OKB
OKB  NEAR Protocol
NEAR Protocol  Aptos
Aptos  Cronos
Cronos  BlackRock USD Institutional Digital Liquidity Fund
BlackRock USD Institutional Digital Liquidity Fund  Jito Staked SOL
Jito Staked SOL  Ondo
Ondo  Ethereum Classic
Ethereum Classic